Through the Settings section of a config, you can configure the following parameters of the anomaly detection service:
- Anomaly score outside data range - specific anomaly score fo values outside the expected data range of particular query
- Parallelization - number of workers to run workloads in parallel
- State restoration - whether to restore models’ state in between runs if the service is restarted or stopped
Anomaly Score Outside Data Range #
This argument allows you to override the anomaly score for anomalies that are caused by values outside the expected data range of particular query . The reasons for such anomalies can be various, such as improperly constructed metricsQL queries, sensor malfunctions, or other issues that lead to unexpected values in the data and require investigation.
If not set, the
anomaly score
for such anomalies defaults to 1.01 for backward compatibility, however, it is recommended to set it to a higher value, such as 5.0, to better reflect the severity of anomalies that fall outside the expected data range to catch them faster and check the query for correctness and underlying data for potential issues.
Here’s an example configuration that sets default anomaly score outside expected data range to 5.0 and overrides it for a specific model to 1.5:
settings:
n_workers: 4
restore_state: True # restore state from previous run, if available
anomaly_score_outside_data_range: 5.0
schedulers:
periodic:
class: periodic
fit_every: 5m
fit_window: 3h
infer_every: 30s
# other schedulers
models:
zscore_online_override:
class: zscore_online
z_threshold: 3.5
clip_predictions: True
# will be inherited from settings.anomaly_score_outside_data_range
# anomaly_score_outside_data_range: 5.0
zscore_online_override:
class: zscore_online
z_threshold: 3.5
clip_predictions: True
anomaly_score_outside_data_range: 1.5 # will override settings.anomaly_score_outside_data_range
# other models
reader:
class: vm
datasource_url: 'https://play.victoriametrics.com'
tenant_id: "0"
queries:
error_rate:
expr: 'rand()*100 + rand()' # example query that generates values between 1 and 100 and sometimes exceeds 100
data_range: [0., 100.] # expected data range for the underlying query and business logic
# other queries
sampling_period: 30s
latency_offset: 10ms
query_from_last_seen_timestamp: False
verify_tls: False
# other reader settings
writer:
class: "vm"
datasource_url: http://localhost:8428
metric_format:
__name__: "$VAR"
for: "$QUERY_KEY"
# other writer settings
monitoring:
push:
url: http://localhost:8428
push_frequency: 1m
# other monitoring settings
Parallelization #
The n_workers argument allows you to explicitly specify the number of workers for internal parallelization of the service. This can help improve performance on multicore systems by allowing the service to process multiple tasks in parallel. For backward compatibility, it’s set to 1 by default, meaning that the service will run in a single-threaded mode. It should be an integer greater than or equal to -1, where -1 and 0 means that the service will automatically inherit the number of workers based on the number of available CPU cores.
Increasing the number can be particularly useful when dealing with a high volume of queries returning many (long) timeseries. Decreasing the number can be useful when running the service on a system with limited resources or when you want to reduce the load on the system.
Here’s an example configuration that uses 4 workers for service’s internal parallelization:
settings:
n_workers: 4
restore_state: False # do not restore state from previous run
schedulers:
periodic:
class: periodic
fit_every: 5m
fit_window: 3h
infer_every: 30s
# other schedulers
models:
zscore_online_override:
class: zscore_online
z_threshold: 3.5
clip_predictions: True
# other models
reader:
class: vm
datasource_url: 'https://play.victoriametrics.com'
tenant_id: "0"
queries:
example_query:
expr: 'rand() + 1' # example query that generates random values between 1 and 2
data_range: [1., 2.]
# other queries
sampling_period: 30s
latency_offset: 10ms
query_from_last_seen_timestamp: False
verify_tls: False
# other reader settings
writer:
class: "vm"
datasource_url: http://localhost:8428
metric_format:
__name__: "$VAR"
for: "$QUERY_KEY"
# other writer settings
monitoring:
push:
url: http://localhost:8428
push_frequency: 1m
# other monitoring settings
State Restoration #
This feature is best used with config hot-reloading Available from v1.25.0 for increased deployment flexibility.
The restore_state argument
Available from v1.24.0
makes vmanomaly service stateful by persisting and restoring state between runs. If enabled, the service will save the state of anomaly detection models and their training data to local filesystem, allowing for seamless continuation of operations after service restarts.
By default, restore_state is set to false, meaning the service will start fresh on each restart, to maintain backward compatibility.
This feature requires enabling
on-disk mode
for the models and data. If not enabled, the service will exit with an error when restore_state is set to true.
Benefits #
This feature improves the experience of using the anomaly detection service in several ways:
- Operational continuity: Production of anomaly scores is resumed from the last known state, minimizing downtime, especially useful in conbination with
periodic schedulers
with
start_fromargument explicitly defined. - Resource efficiency: Avoids unnecessary resource and time consumption by not retraining models that have already been trained and remain actual, or querying redundant data from VictoriaMetrics TSDB.
- Config hot-reloading: Allows for on-the-fly configuration changes with the reuse of unchanged models/data/scheduler combinations, avoiding unnecessary retraining, additional resource utilization and manual service restarts. Please refer to the hot-reload section for more details on how to use this feature.
How it works #
Storage: The service dumps its state into a database file located at $VMANOMALY_MODEL_DUMPS_DIR/vmanomaly.db. This database contains metadata about model configurations, schedulers and references to the trained model instances and their respective data.
State restoration: When the service starts with restore_state set to true, it will:
- Check for the existence of the database file in the specified directory.
- If the file does not exist, it will create a new database file and initialize the state with the current configuration, training models as needed. If the file exists, then it compares the loaded state with the current configuration to ensure compatibility - what can be reused and what needs to be retrained (e.g., if the model class or hyperparameters have changed, it will not restore the state for that model, same for schedulers or reader queries). For reusable components, previously saved state, including model configurations, trained model instances, and their training data, will be restored.
- Subsequently, it will check for model “staleness” and retrain models if necessary, based on the current configuration and the last training time stored in the database vs next scheduled training time. If the model is actual, it will continue to use the previously trained model instances or its training data. If the model is stale (e.g.
fit_everytime has passed since the last training), it will retrain the model using the latest data offit_windowlength from VictoriaMetrics TSDB.
State update: The service periodically saves the updated state after each “atomic” operations, such as (model_alias, query_alias)-based training or inference. This ensures that the state is always up-to-date and can be restored in case of a service restart. Online models are also updated after each inference, while offline models are only saved after each training operation as they do not change the state during consecutive fit calls.
Cleanup behavior: When restore_state is switched from true to false, the database file is automatically removed on the next service startup to prevent inconsistent behavior. All the artifacts (such as model dumps and data dumps) will be removed as well, so the service will start fresh without any previous state.
Here’s an example configuration that enables state restoration:
settings:
restore_state: true
n_workers: 4
schedulers:
periodic:
class: periodic
fit_every: 5m
fit_window: 3h
infer_every: 30s
# other schedulers
models:
zscore_online:
class: zscore_online
z_threshold: 3.5
clip_predictions: True
# other models
reader:
class: vm
datasource_url: 'https://play.victoriametrics.com'
tenant_id: "0"
queries:
example_query:
expr: 'rand() + 1' # example query that generates random values between 1 and 2
data_range: [1., 2.]
# other queries
sampling_period: 30s
latency_offset: 10ms
query_from_last_seen_timestamp: False
verify_tls: False
# other reader settings
writer:
class: "vm"
datasource_url: http://localhost:8428
metric_format:
__name__: "$VAR"
for: "$QUERY_KEY"
# other writer settings
monitoring:
push:
url: http://localhost:8428
push_frequency: 1m
# other monitoring settings
Example #
For a configuration with the following models, queries and schedulers:
settings:
n_workers: 4
restore_state: True # enables state restoration
schedulers:
periodic_1d:
class: periodic
fit_every: 1h
infer_every: 30s
fit_window: 24h
models:
zscore_online:
class: zscore_online
z_threshold: 3.5
schedulers: ['periodic_1d']
prophet:
class: prophet
schedulers: ['periodic_1d']
queries: ['q1', 'q2']
args:
interval_width: 0.98
reader:
class: vm
datasource_url: 'https://play.victoriametrics.com'
tenant_id: "0"
queries:
q1:
expr: 'some_metricsql_query_1'
q2:
expr: 'some_metricsql_query_2'
sampling_period: 30s
# other components like writer, monitoring, etc.
if the service is restarted in less than 1 hour after the last training (now < next scheduled fit time), it will restore the state of the zscore_online and prophet models if their signature (class, hyperparameters, schedulers, etc.) has not changed. It will load the trained model instances or their training data from disk and continue producing
anomaly scores
without retraining. If there are changes or new queries added to the configuration, the service will add these to scheduled jobs for fit and infer. That’s what is changed and what is restored in a config below:
settings:
n_workers: 2 # changed, but does not affect state restoration
restore_state: True # enables state restoration, still enabled
schedulers:
periodic_1d: # can be fully reused, no changes
class: periodic
fit_every: 1h # unchanged, still fits every hour
infer_every: 30s # unchanged, still infers every 30 seconds
fit_window: 24h # unchanged, still fits on the last 24 hours of data
models:
zscore_online: # can't be reused, because its `z_threshold` has changed
class: zscore_online # unchanged, still the same model class
z_threshold: 3.0 # changed, needs retraining!
schedulers: ['periodic_1d'] # unchanged, still attached to the same scheduler
prophet: # can be partially reused, because its class and schedulers are unchanged but queries have changed
class: prophet # unchanged, still the same model class
schedulers: ['periodic_1d'] # unchanged, still attached to the same scheduler
queries: ['q1', 'q3'] # changed, added new query 'q3', drops 'q2', so (prophet, q2) should be trained from scratch
args:
interval_width: 0.98 # unchanged, still the same argument
reader: # can be partially reused, because its class and datasource URL are unchanged, but queries have changed
class: vm # unchanged, still the same reader class
datasource_url: 'https://play.victoriametrics.com' # unchanged, still the same datasource URL
tenant_id: "0" # unchanged, still the same tenant ID
queries:
q1:
expr: 'some_metricsql_query_1' # unchanged, still the same query
q2:
expr: 'some_metricsql_query_2' # will be removed, no longer used by any model
q3:
expr: 'some_metricsql_query_3' # new query, added to the reader, and used by the `prophet` model
sampling_period: 30s # unchanged, still the same sampling period
# other components like writer, monitoring, etc. remain unchanged
This means that the service upon restart:
- Won’t restore the state of
zscore_onlinemodel, because itsz_thresholdargument has changed, retraining from scratch is needed on the lastfit_window= 24 hours of data forq1,q2andq3(as model’squeriesarg is not set so it defaults to all queries found in the reader). - Will partially restore the state of
prophetmodel, because its class and schedulers are unchanged, but only instances trained on timeseries returned byq1query. New fit/infer jobs will be set for new queryq3. The old queryq2artifacts will be dropped upon restart - all respective models and data for (prophet,q2) combination will be removed from the database file and from the disk.
Retention #
Available from v1.28.1
The retention argument allows to set a time-to-live
(TTL) for service artifacts, such as stored model instances and their training data. When enabled, the service will periodically check (controlled by check_interval period) and clean up model instances that have not been used for inference or refitting within the specified period of time (defined in ttl argument as a valid period). This helps to manage resources in long-running deployments by removing stale or unused artifacts.
Use Cases #
- With online models
as they continuously create model instances for new timeseries over time during inference calls, especially when combined with
periodic schedulers
with infrequent
fit_every(say,90d). - In deployments where the set of monitored timeseries changes frequently, leading to accumulation of unused model instances and training data over time, due to high churn rate or relabeling of metrics.
- When using state restoration feature which improves fault tolerance, but may retain all model instances and their training data for considerable time, potentially leading to high disk or RAM usage.
Configuration #
The section is backward-compatible and disabled by default, meaning that all model instances and their training data are retained unless:
- The service is restarted with
restore_stateset tofalse, which triggers a cleanup of all stored artifacts. - The models are marked as outdated once scheduled re-fitting is due, leading to retraining and replacement of previous artifacts.
ttl argument defines the time-to-live period for model instances and their training data. It should be a valid period string (e.g., 7d for 7 days, 30d for 30 days, etc.). If a model instance or its training data has not been used for inference or refitting within this period, it will be considered stale and eligible for cleanup.
If set higher than respective scheduler’s fit_every period, the ttl will have no effect, as models will always be refitted before they become stale.
check_interval argument defines how often the service should check for stale artifacts. It should be a valid period string (e.g., 1h for 1 hour, 24h for 24 hours, etc.). During each check, the service will evaluate all stored model instances and their training data against the defined ttl and remove those that are stale.
Check interval should be set to a value smaller than ttl and smaller than the smallest fit_every period among all schedulers used in the config to ensure timely cleanup of stale artifacts, otherwise stale artifacts may persist longer than intended.
Example #
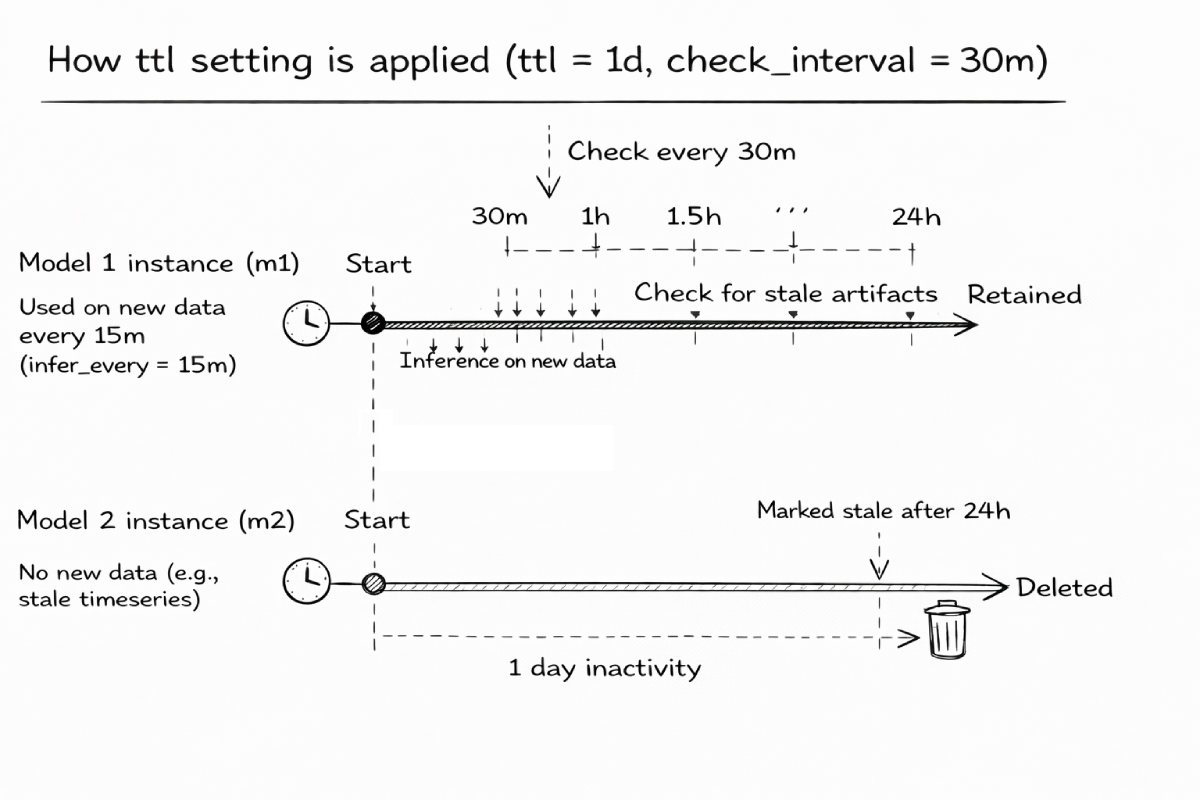
Here’s an example configuration that enables retention with a TTL of 1 day and a check interval of 30 minutes, where inference is performed every 15 minutes.
- Model instances and their training data that have not been used for inference or refitting within the last day will be cleaned up every 30 minutes (m2 example on a diagram)
- While model instances used for inference within the last day at least 1 time will be retained (m1 example on a diagram)
schedulers:
s1:
class: periodic
infer_every: 15m
# other scheduler args
# other schedulers
reader:
class: vm
datasource_url: 'https://play.victoriametrics.com'
tenant_id: "0"
queries:
q1:
expr: 'some_metricsql_query_1' # returns active timeseries
q2:
expr: 'some_metricsql_query_2' # returns high-churn timeseries
sampling_period: 30s
# other reader args
models:
m1: # model instances will be retained due to stable data returned by q1
class: zscore_online
schedulers: ['s1']
queries: ['q1']
# other model args
m2: # model instances will be likely dropped during retention checks due to high churn rate
class: prophet
schedulers: ['s1']
queries: ['q2']
# other model args
# other models
# other sections like schedulers, models, reader, writer, monitoring, etc.
settings:
# other settings
restore_state: True # enables state restoration
retention:
ttl: 24h # time-to-live for model instances and their training data
check_interval: 30m # interval to check for stale artifacts
Logger Levels #
Available from v1.25.3
vmanomaly service supports per-component logger levels, allowing to control the verbosity of logs for each component independently. This can be useful for debugging or monitoring specific components without overwhelming the logs with information from other components. Prefixes are also supported, allowing to set the logger level for all components with a specific prefix.
The logger levels can be set in the settings section of the config file under logger_levels key, where the key is the component name or prefix and the value is the desired logger level. The available logger levels are: debug, info, warning, error, and critical.
Best used in combination with hot-reload to change the logger levels on-the-fly without restarting the service through a short-circuit config check than doesn’t even trigger the state restoration logic.
Here’s an example configuration that sets the logger level for the reader component to debug and for the writer component to critical, while --loggerLevel
command line argument
sets the default logger level to INFO for all (the other) components, unless overridden by the config:
If commented out in hot-reload mode during hot-reload event, the logger level for the component will be set back to what --loggerLevel command line argument is set to, which defaults to info if not specified.
settings:
n_workers: 4
restore_state: True # enables state restoration
logger_levels:
reader.vm: DEBUG # affects only VmReader logs
model: WARNING # applies to all components with 'model' prefix, such as 'model.zscore_online', 'model.prophet', etc.
# once commented out in hot-reload mode, will use the default logger level set by --loggerLevel command line argument
# monitoring.push: critical