Overview #
Ensuring
high availability
and
horizontal scalability
is important for maintaining reliable anomaly detection in distributed environments. Horizontal scalability allows vmanomaly to distribute workloads across multiple nodes by sharding configuration entities, preventing performance bottlenecks. High availability ensures redundancy by replicating
sub-configurations
across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of data loss or service disruption due to node failures.
This document explains how vmanomaly achieves scalability through sharding and redundancy through replication, covering configurations for Docker, Docker Compose, and Helm deployments.
Global Configuration #
vmanomaly service operations are configured using YAML files that define various
components
, as shown in the example below. These (global) configurations can be divided into smaller, fully functional
sub-configurations
, which can be used for
horizontal scalability
through sharding or for
high availability
by enabling replication.
Configuration example #
# https://docs.victoriametrics.com/anomaly-detection/components/scheduler/
schedulers:
periodic_1d: # alias
class: 'periodic' # scheduler class
infer_every: "30s"
fit_every: "1h"
fit_window: "24h"
# https://docs.victoriametrics.com/anomaly-detection/components/models/
models:
zscore: # we can set up alias for model
class: 'zscore' # model class
z_threshold: 3.5
queries: ['cpu_seconds_total', 'host_network_receive_errors']
# https://docs.victoriametrics.com/anomaly-detection/components/reader/#vm-reader
reader:
datasource_url: "https://play.victoriametrics.com/"
tenant_id: "0:0"
class: 'vm'
sampling_period: "30s" # what data resolution to fetch from VictoriaMetrics' /query_range endpoint
queries: # aliases to MetricsQL expressions
cpu_seconds_total:
expr: 'avg(rate(node_cpu_seconds_total[5m])) by (mode)'
host_network_receive_errors:
expr: 'rate(node_network_receive_errs_total[3m]) / rate(node_network_receive_packets_total[3m])'
# https://docs.victoriametrics.com/anomaly-detection/components/writer/
writer:
datasource_url: "http://victoriametrics:8428/"
Sub-configuration #
Global configuration
file can be split into N >= 1 validated sub-configurations based on logical entities such as
schedulers
,
queries
,
models
, and
extra_filters
. Each sub-configuration remains functional and respects the many-to-many relationships between models, queries, and schedulers. A minimal valid sub-configuration consists of a single
model type
running on a single
query
and attached to a single
scheduler
.
Example config above can be split into 2 sub-configurations (by queries):
- 1 model type (
zscore), attached to 1 scheduler (periodic_1d) which is run on 1st query (cpu_seconds_total) - 1 model type (
zscore), attached to 1 scheduler (periodic_1d) which is run on 2nd query (host_network_receive_errors)
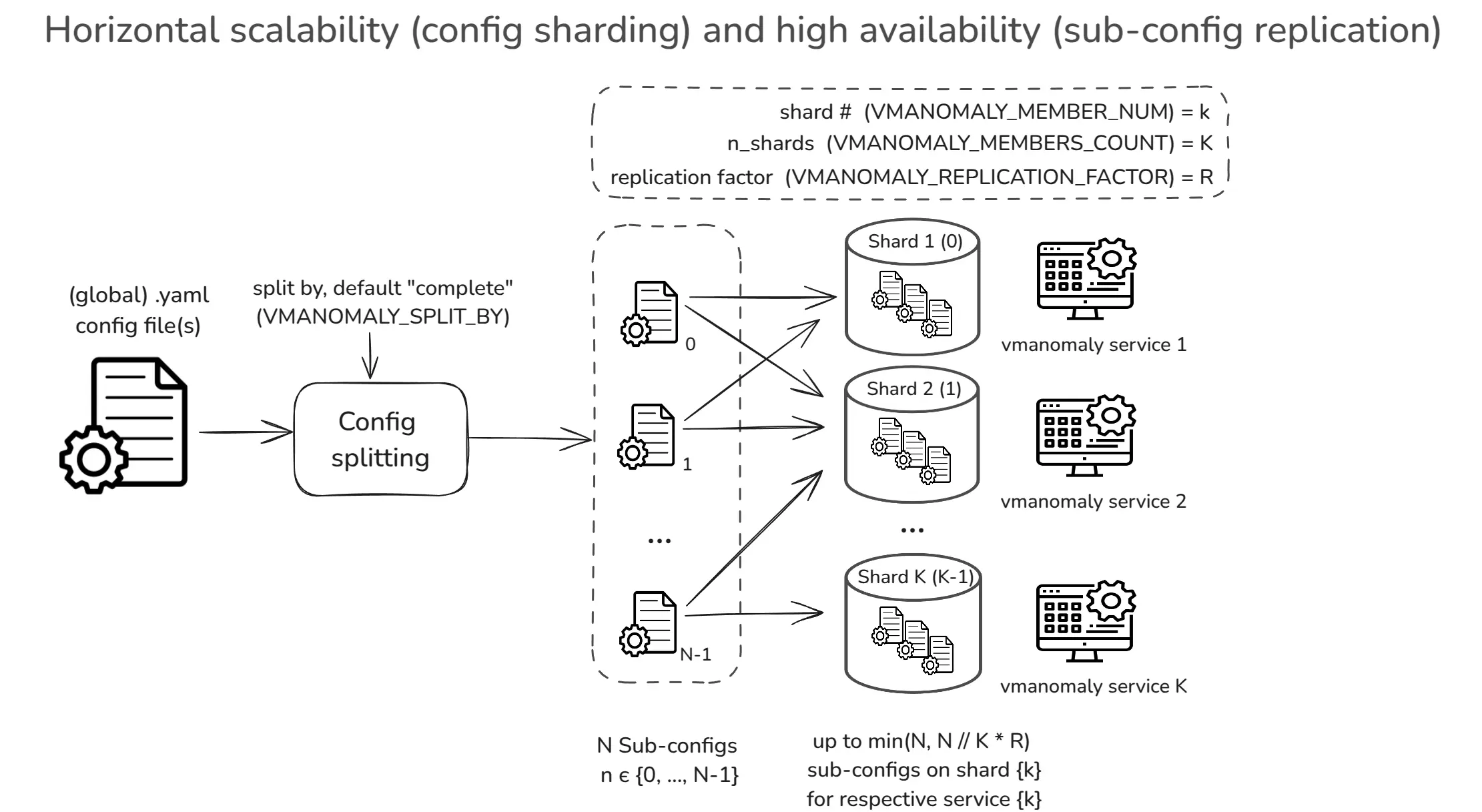
Horizontal Scalability #
vmanomaly supports horizontal scalability
Available from v1.21.0
by sharding
sub-config entities
, enabling workload distribution across multiple nodes while preserving consistency and maintaining a single global configuration entry point.
A vmanomaly
global YAML configuration
can be split into N validated
sub-configurations
based on logical entities such as
schedulers
,
queries
,
models
, and
extra_filters
.
These
sub-configurations
can be assigned to a specific shard (node) indexed from {0, K-1} across K available nodes.
Additionally, a replication factor R ≥ 1 ensures
high availability
by enforcing redundancy across shards.
Please refer to deployment options section for the examples (Docker, Docker Compose, Helm). To avoid duplicate metrics being reported from each vmanomaly service used in sharded mode, make sure that deduplication is configured on vmsingle or vmselect and vmstorage for the VictoriaMetrics instance used in the writer section of the configuration .
Sharding configuration can be controlled by using the following environment variables:
VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT: Defines the total number of shards (i.e., available nodes to distribute sub-configurations to).
Defaults to1for backward compatibility.VMANOMALY_MEMBER_NUM: Specifies the shard index (0toVMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT - 1), determining the subset of sub-configurations to run on a specific node. Defaults to0. Supports automatic pod name discovery in Kubernetes StatefulSets (e.g., if set tovmanomaly-node-exporter-7, shard7will be extracted).VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR: IfR > 1, enables high availability by ensuring each sub-configuration is assigned to exactlyRshards. Defaults to1(no replication).VMANOMALY_SPLIT_BY: Defines the logical entity used to split the global config into sub-configurations . Defaults tocomplete, which provides the most granular distribution (1 model per sub-config , mapped to 1 query and attached to 1 scheduler) for balanced workloads.
The total number of available and assigned sub-configurations per shard can be found using the following self-monitoring metric:
# HELP vmanomaly_config_entities Number of sub-configs (entities) in the configuration available for sharding.
Scope: total - total number of entities, shard - number of entities used on the current shard.
# TYPE vmanomaly_config_entities gauge
vmanomaly_config_entities{preset="default",scope="total"} 8.0
vmanomaly_config_entities{preset="default",scope="shard"} 4.0
Meaning, vmanomaly runs in sharded mode, where this particular shard uses 4 out of 8
sub-configurations
, received after
global config
split.
For more details, refer to the vmanomaly_config_entities
self-monitoring metric
.
Example #
For a
global configuration
that is split into 9
sub-configs
[1, 2, 3, ..., 9], setting:
VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT = 3(3 shards)VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR = 1(default, no replication)
results in the following distribution of sub-configs across the shards (nodes):
- Node 1 (index 0):
[1, 4, 7] - Node 2 (index 1):
[2, 5, 8] - Node 3 (index 2):
[3, 6, 9]
Since the replication factor is set to 1, each
sub-config
is assigned to exactly one node, meaning there is no redundancy in the distribution.
High Availability #
Similar to other VictoriaMetrics ecosystem components, like
VMAgent
or
VMAlert
, there exists a support for high availability in vmanomaly through
sub-config
replication
Available from v1.21.0
.
When VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR > 1, each
sub-config
n from {0, N-1} is assigned to exactly R nodes. This ensures redundancy, preventing single-node failures from causing data loss.

Please refer to deployment options section for the examples (Docker, Docker Compose, Helm). To avoid duplicate metrics being reported from each vmanomaly service used in sharded mode, make sure that deduplication is configured on vmsingle or vmselect and vmstorage for the VictoriaMetrics instance used in the writer section of the configuration .
Example #
For a
global configuration
split into 9
sub-configs
[1, 2, 3, ..., 9], with:
VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT = 3(3 shards)VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR = 2(each sub-config is assigned to exactly 2 nodes)
the resulting replicated sharded distribution is:
- Node 1 (index 0):
[1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9] - Node 2 (index 1):
[1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8] - Node 3 (index 2):
[2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9]
Now, each sub-config (1–9) is present on exactly 2 nodes, ensuring redundancy:
- Sub-config 5 appears on nodes 2 & 3
- Sub-config 7 appears on nodes 1 & 2
- Sub-config 9 appears on nodes 1 & 3, etc.
Deployment Options #
To enable horizontal scalability (HS) or high availability (HA) in vmanomaly, deployment settings should be accordingly configured. Below are examples for running vmanomaly with sharding and replication using
Docker
,
Docker Compose
, and
Helm
.
Docker #
To run vmanomaly in a Docker container with sharding enabled (e.g., setting VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT=2 for two shards and VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR=1 for no replication), specify the shard index using VMANOMALY_MEMBER_NUM. Indexing starts from 0 up to VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT - 1. The example below runs the first shard (VMANOMALY_MEMBER_NUM=0):
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -x -e
cd "$(dirname "$0")/.." || exit 1
# run the first shard (VMANOMALY_MEMBER_NUM=0) in a two-shard setup (VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT=2)
docker run -i -t --rm \
--user="$(id -u):$(id -g)" \
--cap-drop=ALL \
-e "VM_LICENSE_FILE=/.secret/license" \
-e "VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT=2" \
-e "VMANOMALY_MEMBER_NUM=0" \
-e "VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR=1"
-e "VMANOMALY_SPLIT_BY=COMPLETE" \
-v "$PWD/global_config.yaml":/global_config.yaml \
-v "$PWD/.secret/license":/.secret/license \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 8490:8490 \
vmanomaly:v1.21.0 \
/global_config.yaml \
--loggerLevel=INFO
Docker Compose #
Sharded vmanomaly can be set up using Docker Compose, enabling easier orchestration of multiple shards. Each shard runs a subset N_k out of N split
sub-configurations
of the global configuration. No replication is set in this example, meaning VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR is set to 1.
The following example demonstrates how to deploy vmanomaly with two shards, each assigned a unique subset of the global config:
# other sections ...
services:
# other services ...
vmanomaly-1:
image: victoriametrics/vmanomaly:v1.21.0
user: "1000:1000"
restart: always
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://127.0.0.1:8490/health"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 5
volumes:
- ./vmanomaly-config:/config
command:
- "/config/global_config.yml"
- "--license=YOUR_LICENSE"
environment:
VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT: 2
VMANOMALY_MEMBER_NUM: 0
VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
VMANOMALY_SPLIT_BY: "COMPLETE"
vmanomaly-2:
image: victoriametrics/vmanomaly:v1.21.0
user: "1000:1000"
restart: always
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://127.0.0.1:8490/health"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 5
volumes:
- ./vmanomaly-config:/config
command:
- "/config/global_config.yml" # Fixed to match vmanomaly-1
- "--license=YOUR_LICENSE"
environment:
VMANOMALY_MEMBERS_COUNT: 2
VMANOMALY_MEMBER_NUM: 1
VMANOMALY_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
VMANOMALY_SPLIT_BY: "COMPLETE"
Helm Charts #
To deploy vmanomaly with N > 1 shards using Helm, ensure chart version 1.9.0
or newer is used. Configure the following settings in values.yaml:
- Set shard count (
.Values.shardsCount): Defines the number of shards (N > 1) to enable horizontal scaling. Configure it here . - (Optional) Enable
high availability
(
.Values.replicationFactor): IfR > 1, each sub-config is assigned to exactlyRshards. Configure it here .
With StatefulSet enabled, vmanomaly automatically extracts shard numbers from pod names. For example, if the pod is named vmanomaly-node-exporter-0, then VMANOMALY_MEMBER_NUM=0 is assigned automatically.