This guide covers OpenShift cluster configuration for collecting and storing logs in Victoria Logs.
Pre-Requirements #
- OpenShift cluster
- Admin access to OpenShift cluster
- kubectl installed and configured to access OpenShift cluster
- Helm installed
Install Red Hat OpenShift Logging operator #
Cluster logging operator is a logging solution to support aggregated cluster logging. It is using Vector for logs collection and shipping to remote storage.
In order to install the operator, navigate to the OpenShift web console and select the Operators tab. Then, click on OperatorHub and search for Red Hat OpenShift Logging. Click on the Red Hat OpenShift Logging operator and then click on Install.
RBAC configuration #
Create a service account and cluster role binding for the service account to access the logs.
OpenShift provides separate ClusterRoles for monitoring of different types of logs: audit, infrastructure and application.
The following configuration will allow the service account to collect all types of logs:
kind: ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: victorialogs
namespace: openshift-logging
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: vl-collect-infra
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: victorialogs
namespace: openshift-logging
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: collect-infrastructure-logs
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: vl-collect-audit
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: victorialogs
namespace: openshift-logging
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: collect-audit-logs
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: vl-collect-application
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: victorialogs
namespace: openshift-logging
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: collect-application-logs
Alternatively, you can use OpenShift console to create the service account and cluster role binding.
Navigate to ServiceAccounts and click on Create Service Account. Fill in the name victorialogs and namespace openshift-logging and click on Create.
Then, navigate to RoleBindings and create a binding for each ClusterRole for subject victorialogs in openshift-logging namespace.
Install Victoria Logs #
Add Victoria Metrics Helm repository :
helm repo add vm https://victoriametrics.github.io/helm-charts/
Minimal configuration for VictoriaLogs running in OpenShift:
securityContext:
enabled: true
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
podSecurityContext:
enabled: true
runAsNonRoot: true
Save the configuration to vl.yaml.
Note, that depending on the OpenShift cluster configuration, additional security settings might be required.
Create namespace for VictoriaLogs:
kubectl create namespace vl
Install VictoriaLogs with the following command:
helm upgrade --namespace vl --install vl vm/victoria-logs-single -f vl.yaml
Configure logs forwarding #
Cluster logging operator uses ClusterLogForwarder resource for logs forwarding configuration.
Here is an example configuration to forward all cluster logs to VictoriaLogs:
apiVersion: observability.openshift.io/v1
kind: ClusterLogForwarder
metadata:
name: logging
namespace: openshift-logging
spec:
managementState: Managed
outputs:
- elasticsearch:
index: logs
url: "http://vl-victoria-logs-single-server.vl.svc.cluster.local:9428/insert/elasticsearch/_bulk?_stream_fields=log_type,hostname,stream,kubernetes.pod_name,kubernetes.container_name,kubernetes.pod_namespace&_time_field=@timestamp&_msg_field=message,msg,_msg,log.msg,log.message,log&fake_field=1"
version: 8
tuning:
compression: gzip
name: victorialogs
type: elasticsearch
- elasticsearch:
index: logs
url: "http://vl-victoria-logs-single-server.vl.svc.cluster.local:9428/insert/elasticsearch/_bulk?_stream_fields=log_type,hostname,annotations.authorization.k8s.io/decision,hostname,verb&_time_field=@timestamp&_msg_field=annotations.authorization.k8s.io/reason&fake_field=1"
version: 8
tuning:
compression: gzip
name: victorialogs-audit
type: elasticsearch
- elasticsearch:
index: logs
url: "http://vl-victoria-logs-single-server.vl.svc.cluster.local:9428/insert/elasticsearch/_bulk?_stream_fields=log_type,hostname,tag,systemd.t.EXE,level&_time_field=@timestamp&_msg_field=message,msg,_msg,log.msg,log.message,log&fake_field=1"
version: 8
tuning:
compression: gzip
name: victorialogs-infrastructure
type: elasticsearch
pipelines:
- inputRefs:
- application
name: application
outputRefs:
- victorialogs-audit
- inputRefs:
- infrastructure
name: infrastructure
outputRefs:
- victorialogs-infrastructure
- inputRefs:
- audit
name: audit
outputRefs:
- victorialogs
serviceAccount:
name: victorialogs
It is also possible to configure logs forwarding using OpenShift console. Navigate to Operators tab and click on Installed Operators. Then, click on Red Hat OpenShift Logging and navigate to ClusterLogForwarders. Click on Create ClusterLogForwarder.
Configure the forwarding to VictoriaLogs using the provided form and click on Create.

Verify logs collection #
To verify that logs are collected and stored in VictoriaLogs, navigate to the VictoriaLogs web interface.
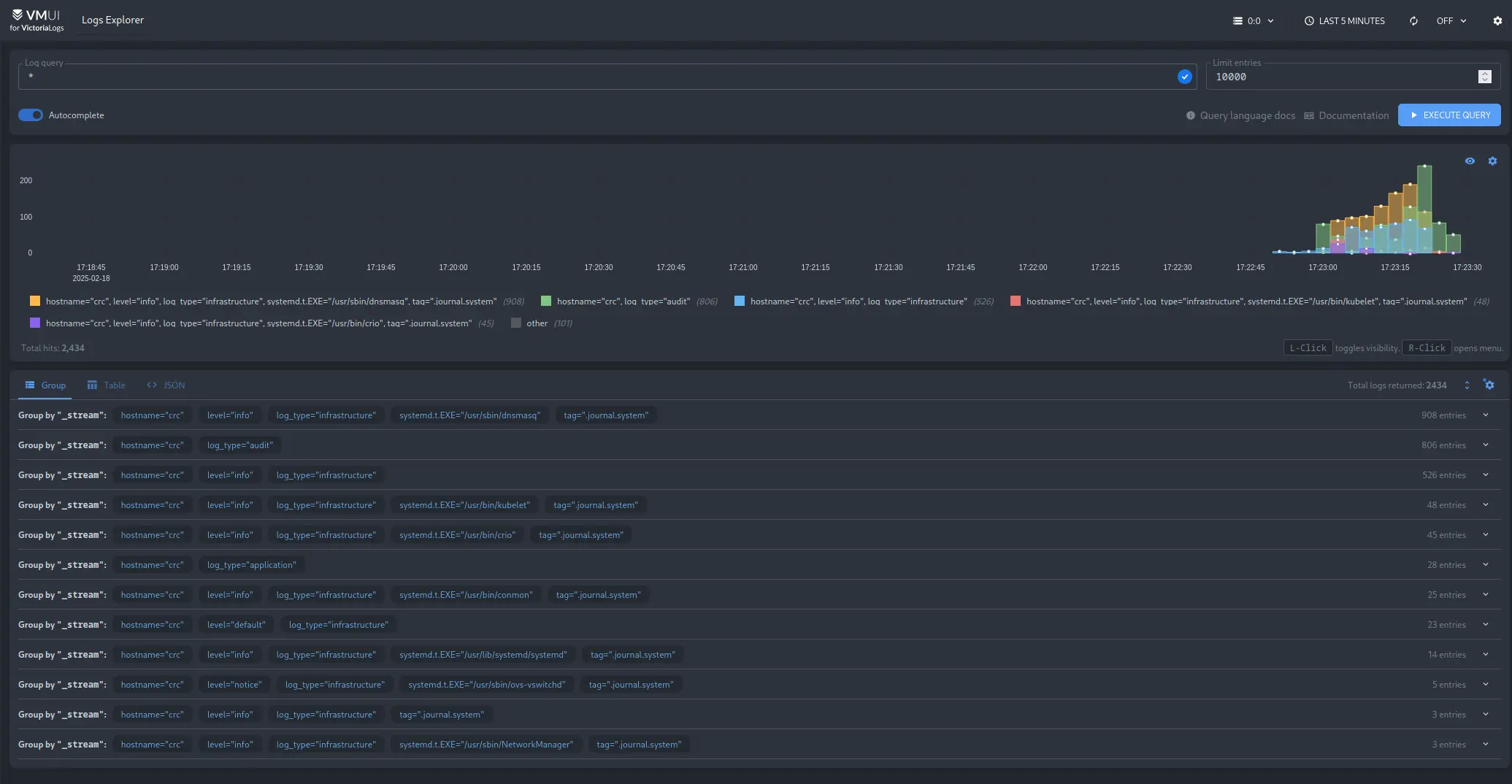
Logs will be available in the interface and can be queried using
LogsQL
.
Note that logs will have log_type attached to them to distinguish between different types of logs.