VictoriaMetrics and VictoriaLogs support ingestion metrics and logs in OpenTelemetry format. This guide covers examples of using opentelemetry-collector and direct pushing of metrics and logs from the Go application.
Pre-Requirements #
Installation #
VictoriaMetrics #
Install VictoriaMetrics helm repo:
helm repo add vm https://victoriametrics.github.io/helm-charts/
helm repo update
Add VictoriaMetrics chart values to convert OTEL metric names to Prometheus canonical format:
cat << EOF > vm-values.yaml
server:
extraArgs:
opentelemetry.usePrometheusNaming: true
EOF
Install VictoriaMetrics single-server version:
helm install victoria-metrics vm/victoria-metrics-single -f vm-values.yaml
Verify it’s up and running:
kubectl get pods
# NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# victoria-metrics-victoria-metrics-single-server-0 1/1 Running 0 3m1s
VictoriaMetrics helm chart provides the following URL for writing data:
Write URL inside the kubernetes cluster:
http://victoria-metrics-victoria-metrics-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local.:8428/<protocol-specific-write-endpoint>
All supported write endpoints can be found at https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/single-server-victoriametrics/#how-to-import-time-series-data.
For OpenTelemetry VictoriaMetrics write endpoint is:
http://victoria-metrics-victoria-metrics-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local.:8428/opentelemetry/v1/metrics
VictoriaLogs #
Install VictoriaLogs:
helm install victoria-logs vm/victoria-logs-single
Verify it’s up and running:
kubectl get pods
# NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# victoria-logs-victoria-logs-single-server-0 1/1 Running 0 1m10s
VictoriaLogs helm chart provides the following URL for writing data:
Write URL inside the kubernetes cluster:
http://victoria-logs-victoria-logs-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local.:9428/<protocol-specific-write-endpoint>
All supported write endpoints can be found at https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victorialogs/data-ingestion/
For OpenTelemetry VictoriaLogs write endpoint is:
http://victoria-logs-victoria-logs-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local.:9428/insert/opentelemetry/v1/logs
OpenTelemetry collector with VictoriaMetrics and VictoriaLogs #
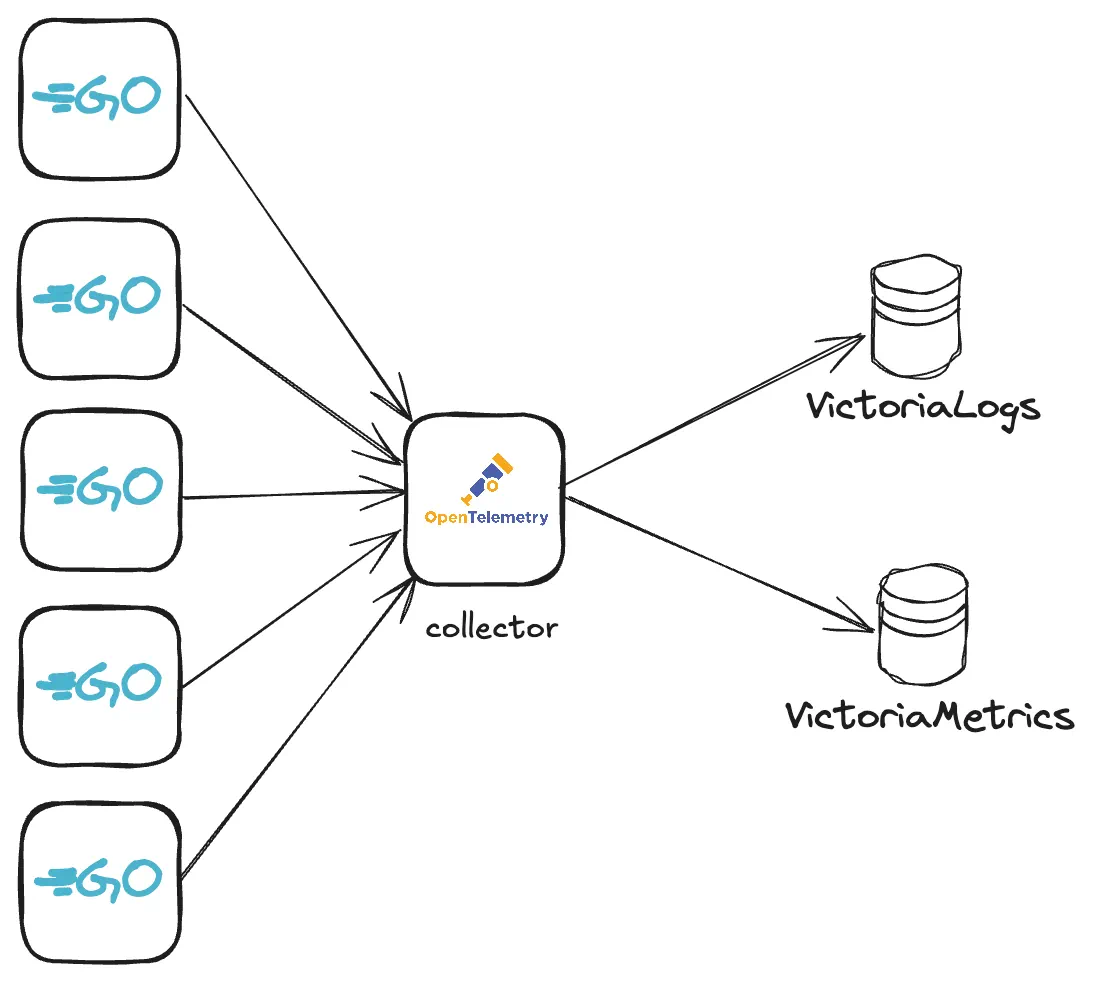
Add OpenTelemetry helm repo:
helm repo add open-telemetry https://open-telemetry.github.io/opentelemetry-helm-charts
helm repo update
Add OpenTelemetry Collector values:
cat << EOF > otel-values.yaml
mode: deployment
image:
repository: "otel/opentelemetry-collector-contrib"
presets:
clusterMetrics:
enabled: true
logsCollection:
enabled: true
config:
# deltatocumulative processor is needed to convert metrics with delta temporality to cumulative temporality.
# VictoriaMetrics doesn't support delta temporality. Skip this processor if you don't use delta temporality.
processors:
deltatocumulative:
max_stale: 5m
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
exporters:
otlphttp/victoriametrics:
compression: gzip
encoding: proto
# Setting below will work for sending data to VictoriaMetrics single-node version.
# Cluster version of VictoriaMetrics will require a different URL - https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/cluster-victoriametrics/#url-format
metrics_endpoint: http://victoria-metrics-victoria-metrics-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local:8428/opentelemetry/v1/metrics
logs_endpoint: http://victoria-logs-victoria-logs-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local:9428/insert/opentelemetry/v1/logs
tls:
insecure: true
service:
pipelines:
logs:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: []
exporters: [otlphttp/victoriametrics]
metrics:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [deltatocumulative]
exporters: [otlphttp/victoriametrics]
EOF
Install OpenTelemetry Collector helm chart:
helm upgrade -i otel open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector -f otel-values.yaml
Check if OpenTelemetry Collector pod is up and running:
kubectl get pod
# NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# otel-opentelemetry-collector-7467bbb559-2pq2n 1/1 Running 0 23m
Forward VictoriaMetrics port to local machine to explore metrics ingested by the collector:
kubectl port-forward svc/victoria-metrics-victoria-metrics-single-server 8428
Visit http://localhost:8428/vmui/#/?g0.expr=k8s_container_ready
to check if metric k8s_container_ready is present.
Check other available metrics by visiting cardinality explorer
page.
Forward VictoriaLogs port to local machine to explore logs ingested by the collector:
kubectl port-forward svc/victoria-logs-victoria-logs-single-server 9428
Visit http://localhost:9428/select/vmui to check if logs ingested by collector are present.
The full version of possible configuration options for the collector can be found in OpenTelemetry docs .
Sending metrics and logs from Go application #
Metrics and logs can be sent via OpenTelemetry instrumentation libraries. You can use any compatible OpenTelemetry instrumentation clients . In our example, we’ll create a WEB server in Golang , instrument it with metrics and logs and configure it to send telemetry data to OpenTelemetry collector. The collector will then forward received data to VictoriaMetrics or VictoriaLogs.
Sending to OpenTelemetry collector #
Create file main.go from example
that implements a dice roll WEB server instrumented with
OpenTelemetry SDK and is configured to send data to OpenTelemetry collector at http://localhost:4318 address.
See how to setup and run OpenTelemetry collector here
.
In the same directory with the file create the go.mod file and execute following commands:
go mod init vm/otel
go mod tidy
Now try running the application:
go run .
By default, the application from example is listening at http://localhost:8080. Start sending requests
to http://localhost:8080/rolldice endpoint to generate some metrics. The following command will send 20 requests:
for i in `seq 1 20`; do curl http://localhost:8080/rolldice; done
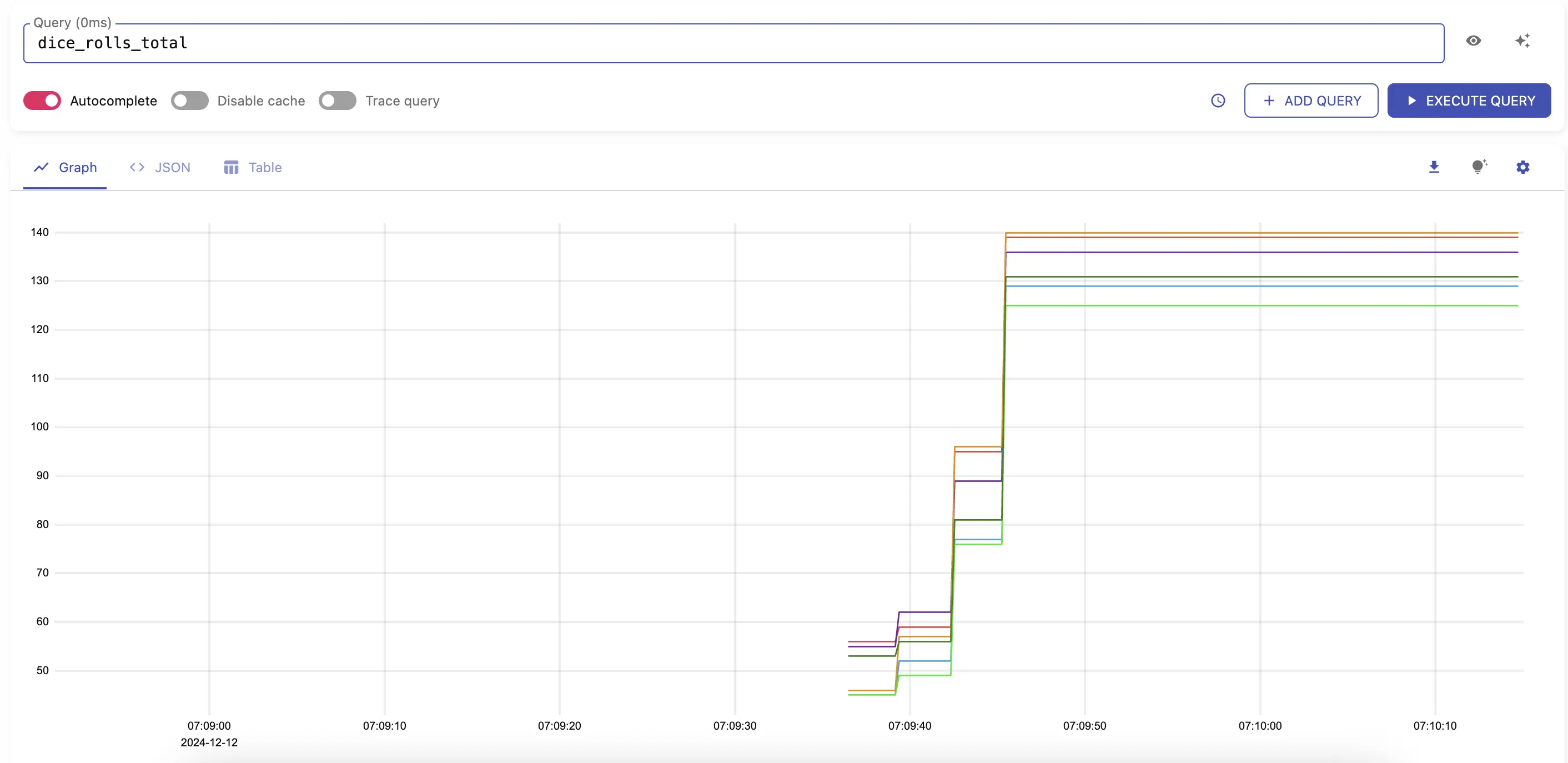
After a few seconds you should start seeing metrics sent to VictoriaMetrics by visiting http://localhost:8428/vmui/#/?g0.expr=dice_rolls_total
in your browser or by querying the metric dice_rolls_total in the UI interface.
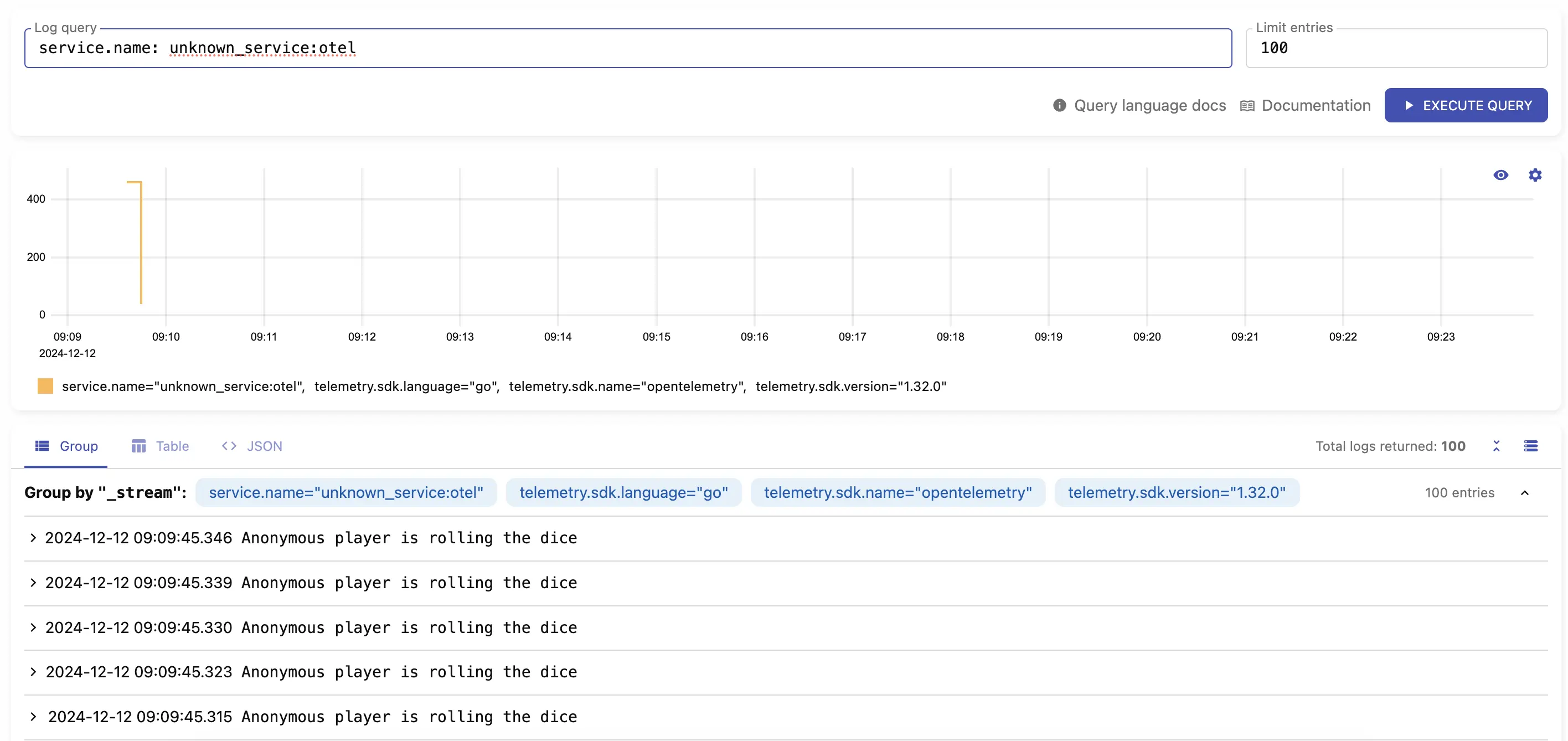
Logs should be available by visiting http://localhost:9428/select/vmui
using query service.name: unknown_service:otel.
Sending without OpenTelemetry collector #
Metrics and logs can be ingested into VictoriaMetrics and VictoriaLogs directly via HTTP requests. Use any compatible OpenTelemetry instrumentation clients .
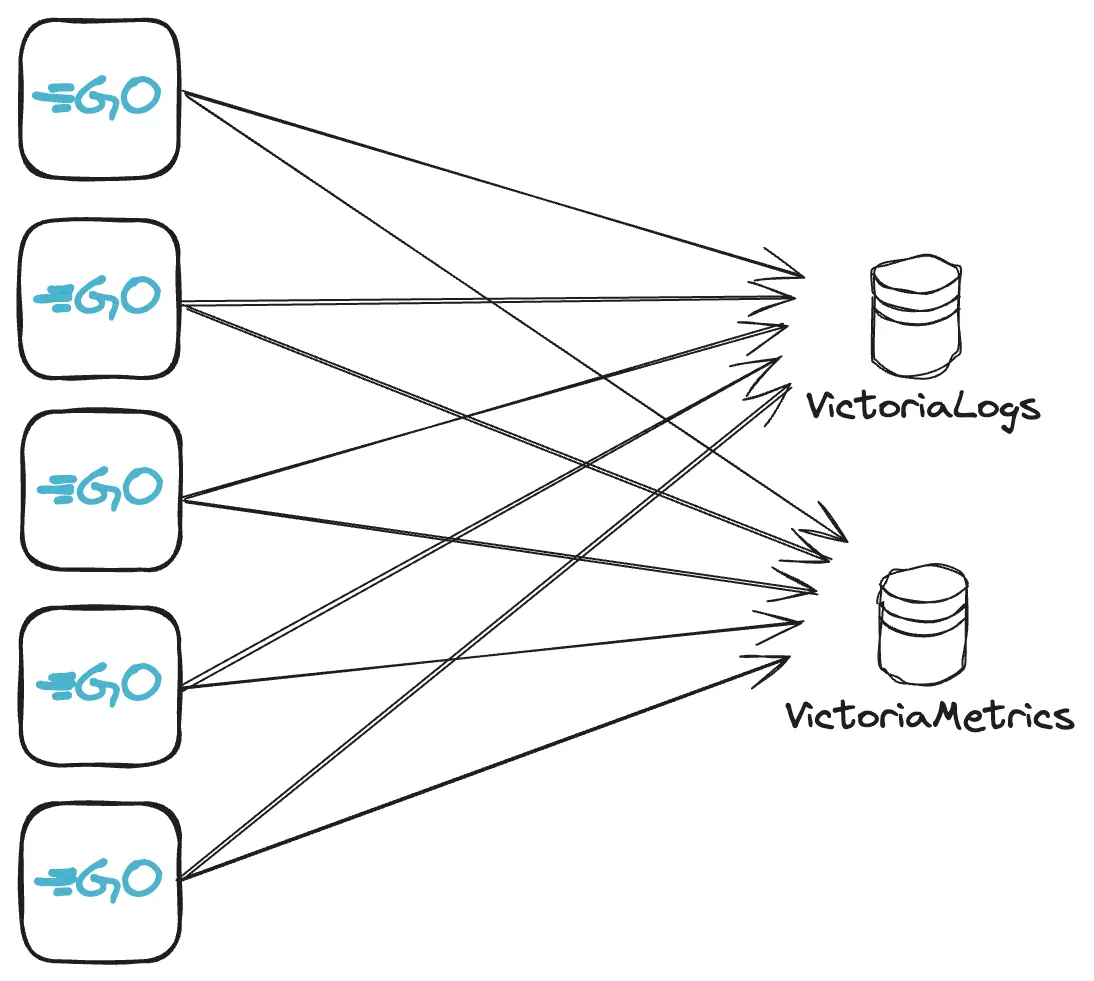
In our example, we’ll create a WEB server in Golang , instrument it with metrics and logs and configure it to send this telemetry data to VictoriaMetrics and VictoriaLogs.
Create file main.go from example
. In the same directory with the file create the go.mod file and execute following commands:
go mod init vm/otel
go mod tidy
The example implements WEB server with two HTTP handlers: /api/slow and /api/fast. Start the application:
go run main.go
2024/03/25 19:27:41 Starting web server...
2024/03/25 19:27:41 web server started at localhost:8081.
Make sure that VictoriaMetrics and VictoriaLogs are available locally at their default ports:
# port-forward victoriametrics to ingest metrics
kubectl port-forward victoria-metrics-victoria-metrics-single-server-0 8428
# port-forward victorialogs to ingest logs
kubectl port-forward victoria-logs-victoria-logs-single-server-0 9428
Visit application links http://localhost:8081/api/fast or http://localhost:8081/api/slow couple of times. The application will generate metrics and logs and will send them to VictoriaMetrics and VictoriaLogs.
After a few seconds you should start seeing metrics sent to VictoriaMetrics by visiting http://localhost:8428/vmui/#/?g0.expr=http_requests_total .
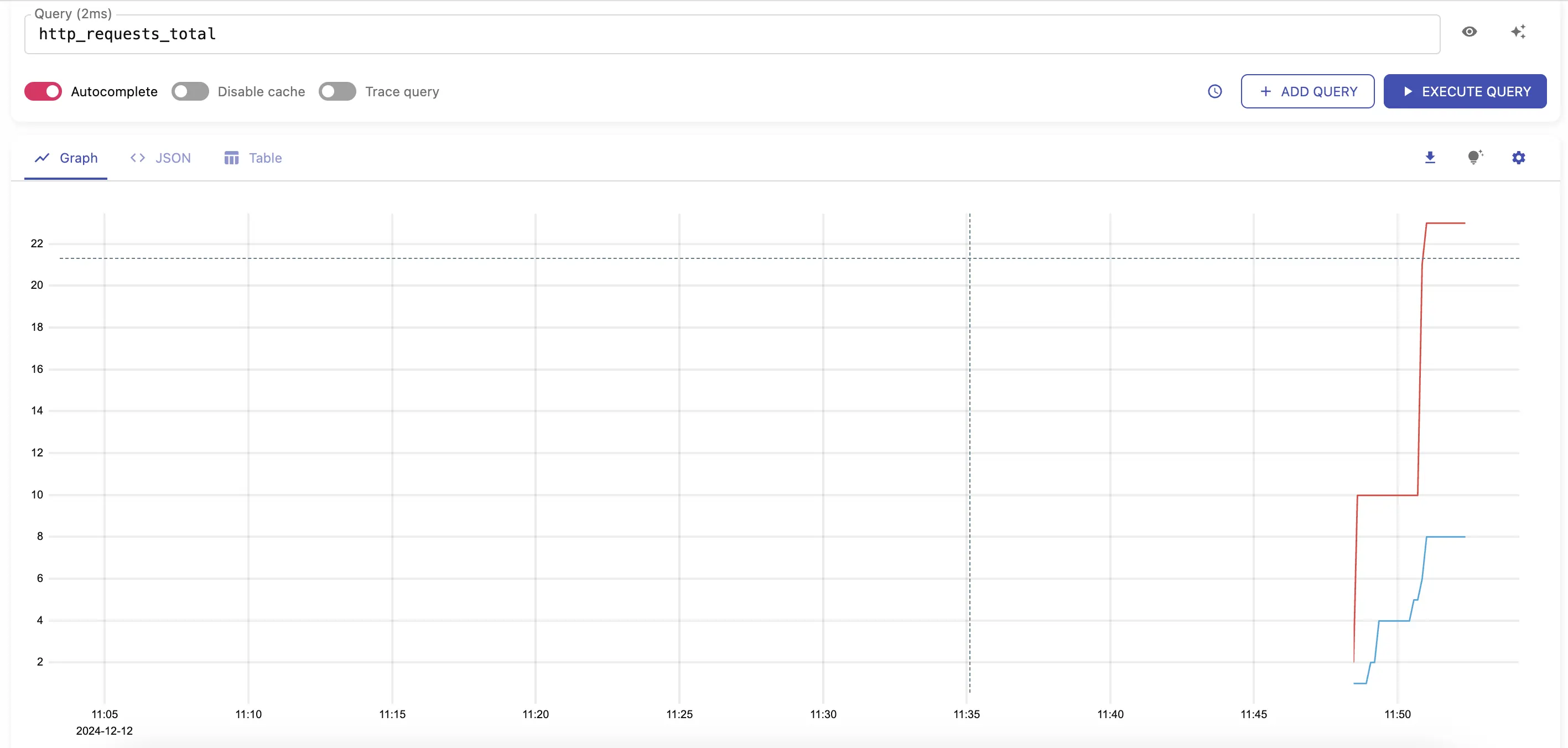
Check other available metrics by visiting cardinality explorer page.
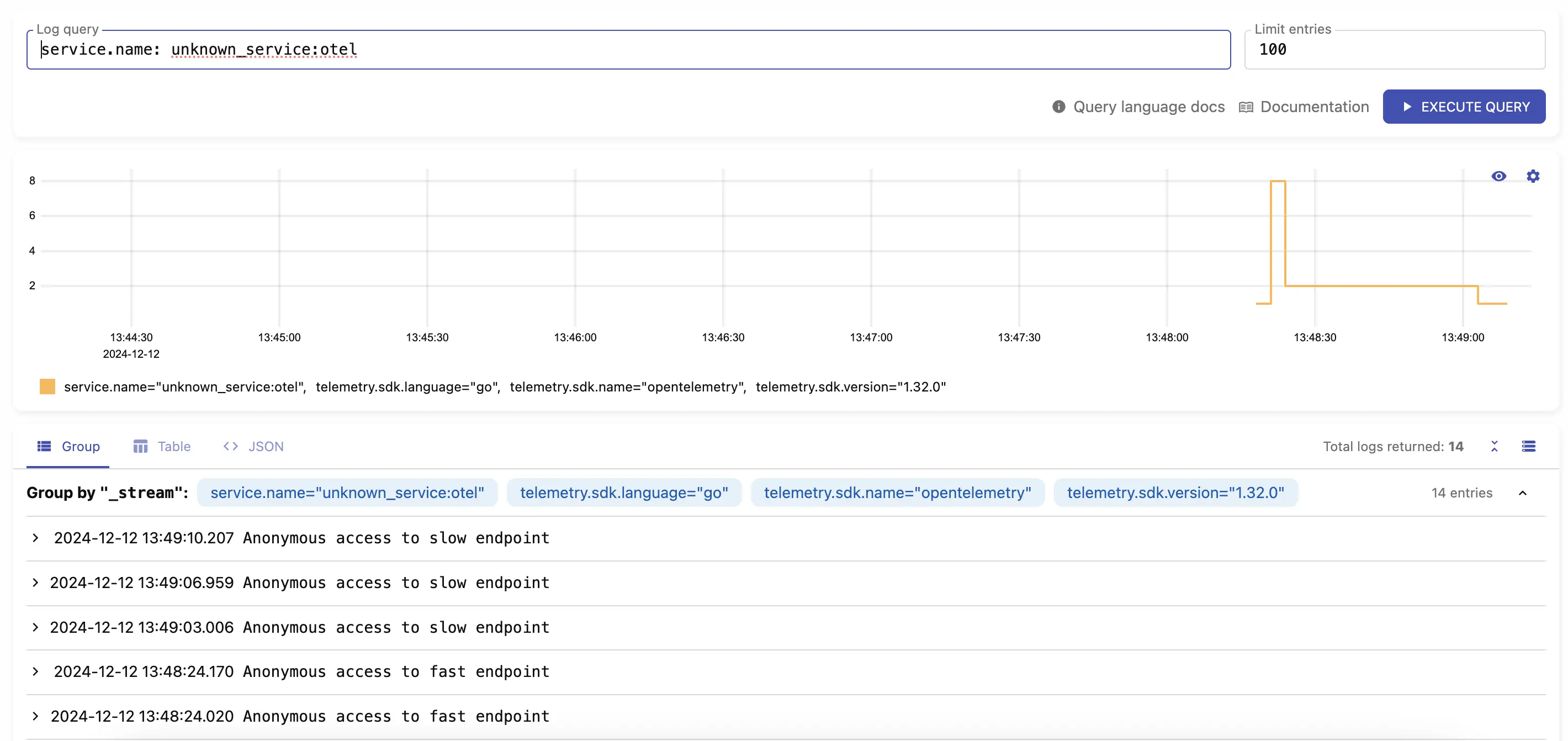
Logs should be available by visiting http://localhost:9428/select/vmui
using query service.name: unknown_service:otel.
Limitations #
- VictoriaMetrics and VictoriaLogs do not support experimental JSON encoding format .
- VictoriaMetrics supports only
AggregationTemporalityCumulativetype for histogram and summary . Either consider using cumulative temporality or trydelta-to-cumulative processorto make conversion to cumulative temporality in OTEL Collector.