This guide covers:
- The setup of a VictoriaMetrics cluster in Kubernetes via Helm charts
- How to scrape metrics from k8s components using service discovery
- How to visualize stored data
- How to store metrics in VictoriaMetrics tsdb
Precondition
We will use:
We use GKE cluster from GCP but this guide is also applied on any Kubernetes cluster. For example Amazon EKS .
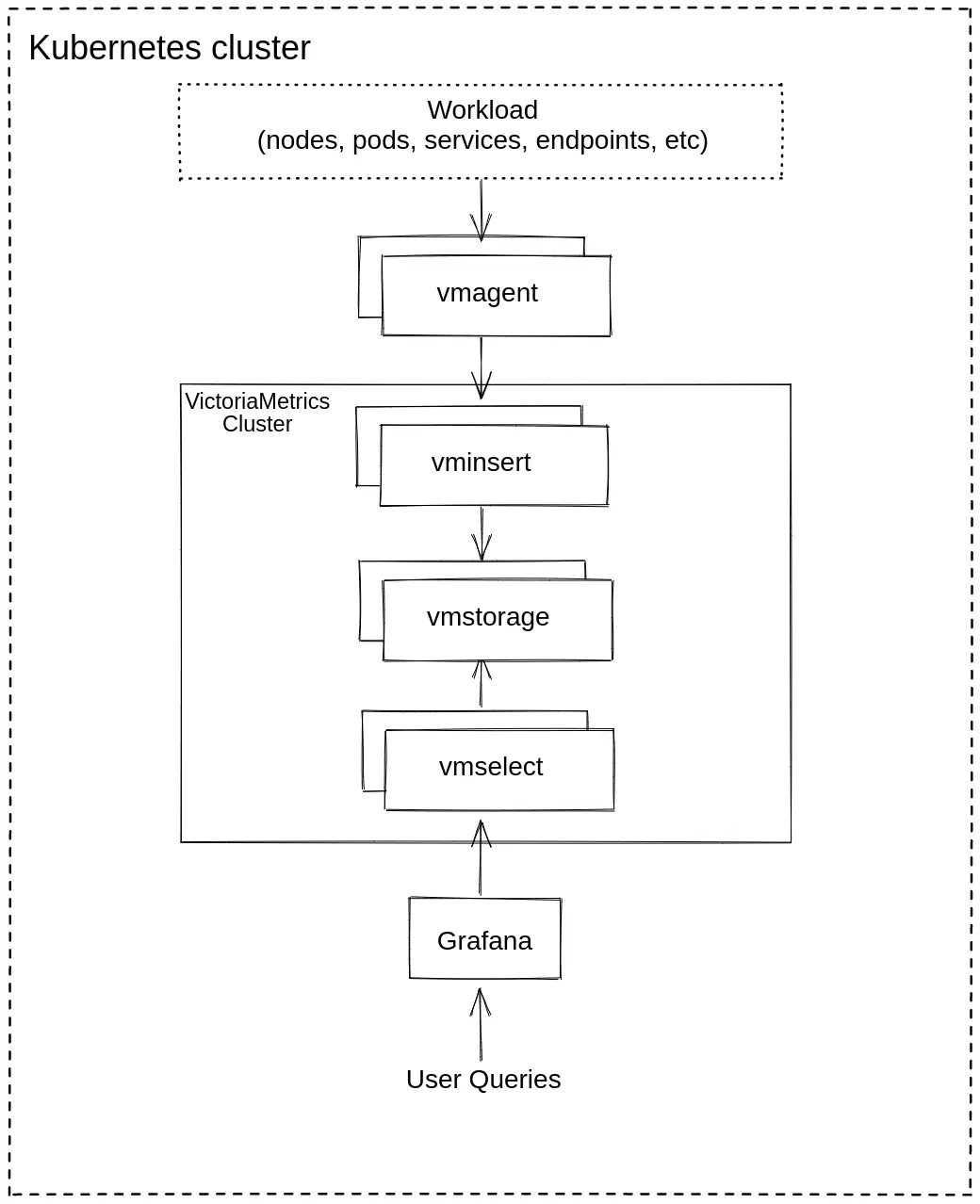
1. VictoriaMetrics Helm repository #
You need to add the VictoriaMetrics Helm repository to install VictoriaMetrics components. We’re going to use VictoriaMetrics Cluster . You can do this by running the following command:
helm repo add vm https://victoriametrics.github.io/helm-charts/
Update Helm repositories:
helm repo update
To verify that everything is set up correctly you may run this command:
helm search repo vm/
The expected output is:
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
vm/victoria-logs-single 0.9.3 v1.16.0 Victoria Logs Single version - high-performance...
vm/victoria-metrics-agent 0.17.2 v1.113.0 Victoria Metrics Agent - collects metrics from ...
vm/victoria-metrics-alert 0.15.0 v1.113.0 Victoria Metrics Alert - executes a list of giv...
vm/victoria-metrics-anomaly 1.9.0 v1.21.0 Victoria Metrics Anomaly Detection - a service ...
vm/victoria-metrics-auth 0.10.0 v1.113.0 Victoria Metrics Auth - is a simple auth proxy ...
vm/victoria-metrics-cluster 0.19.2 v1.113.0 Victoria Metrics Cluster version - high-perform...
vm/victoria-metrics-common 0.0.42 Victoria Metrics Common - contains shared templ...
vm/victoria-metrics-distributed 0.9.0 v1.113.0 A Helm chart for Running VMCluster on Multiple ...
vm/victoria-metrics-gateway 0.8.0 v1.113.0 Victoria Metrics Gateway - Auth & Rate-Limittin...
vm/victoria-metrics-k8s-stack 0.39.0 v1.113.0 Kubernetes monitoring on VictoriaMetrics stack....
vm/victoria-metrics-operator 0.43.0 v0.54.1 Victoria Metrics Operator
vm/victoria-metrics-single 0.15.1 v1.113.0 Victoria Metrics Single version - high-performa...
2. Install VictoriaMetrics Cluster from the Helm chart #
Run this command in your terminal:
cat <<EOF | helm install vmcluster vm/victoria-metrics-cluster -f -
vmselect:
podAnnotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
prometheus.io/port: "8481"
vminsert:
podAnnotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
prometheus.io/port: "8480"
vmstorage:
podAnnotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
prometheus.io/port: "8482"
EOF
- By running
Helm install vmcluster vm/victoria-metrics-clusterwe install VictoriaMetrics cluster to default namespace inside your cluster. - By adding
podAnnotations: prometheus.io/scrape: "true"we enable the scraping of metrics from the vmselect, vminsert and vmstorage pods. - By adding
podAnnotations:prometheus.io/port: "some_port"we enable the scraping of metrics from the vmselect, vminsert and vmstorage pods from their ports as well.
As a result of this command you will see the following output:
NAME: vmcluster
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Mar 21 11:55:50 2025
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Write API:
The Victoria Metrics write api can be accessed via port 8480 with the following DNS name from within your cluster:
vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vminsert.default.svc.cluster.local.
Get the Victoria Metrics insert service URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 8480
You need to update your Prometheus configuration file and add the following lines to it:
prometheus.yml
remote_write:
- url: "http://<insert-service>/insert/0/prometheus/"
for example - inside the Kubernetes cluster:
remote_write:
- url: http://vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vminsert.default.svc.cluster.local.:8480/insert/0/prometheus/
Read API:
The VictoriaMetrics read api can be accessed via port 8481 with the following DNS name from within your cluster:
vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vmselect.default.svc.cluster.local.
Get the VictoriaMetrics select service URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 8481
You need to specify select service URL into your Grafana:
NOTE: you need to use the Prometheus Data Source
Input this URL field into Grafana
http://<select-service>/select/0/prometheus/
for example - inside the Kubernetes cluster:
http://vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vmselect.default.svc.cluster.local.:8481/select/0/prometheus/
For us it’s important to remember the url for the datasource (copy lines from the output).
Verify that VictoriaMetrics cluster pods are up and running by executing the following command:
kubectl get pods
The expected output is:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vminsert-689cbc8f55-95szg 1/1 Running 0 16m
vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vminsert-689cbc8f55-f852l 1/1 Running 0 16m
vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vmselect-977d74cdf-bbgp5 1/1 Running 0 16m
vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vmselect-977d74cdf-vzp6z 1/1 Running 0 16m
vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vmstorage-0 1/1 Running 0 16m
vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vmstorage-1 1/1 Running 0 16m
3. Install vmagent from the Helm chart #
To scrape metrics from Kubernetes with a VictoriaMetrics cluster we need to install vmagent with additional configuration. To do so, please run these commands in your terminal:
helm install vmagent vm/victoria-metrics-agent -f https://docs.victoriametrics.com/guides/examples/guide-vmcluster-vmagent-values.yaml
Here is full file content guide-vmcluster-vmagent-values.yaml
remoteWrite:
- url: http://vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vminsert.default.svc.cluster.local:8480/insert/0/prometheus/
config:
global:
scrape_interval: 10s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: vmagent
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:8429"]
- job_name: "kubernetes-apiservers"
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
relabel_configs:
- source_labels:
[
__meta_kubernetes_namespace,
__meta_kubernetes_service_name,
__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name,
]
action: keep
regex: default;kubernetes;https
- job_name: "kubernetes-nodes"
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics
- job_name: "kubernetes-nodes-cadvisor"
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics/cadvisor
metric_relabel_configs:
- action: replace
source_labels: [pod]
regex: '(.+)'
target_label: pod_name
replacement: '${1}'
- action: replace
source_labels: [container]
regex: '(.+)'
target_label: container_name
replacement: '${1}'
- action: replace
target_label: name
replacement: k8s_stub
- action: replace
source_labels: [id]
regex: '^/system\.slice/(.+)\.service$'
target_label: systemd_service_name
replacement: '${1}'
- job_name: "kubernetes-service-endpoints"
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- action: drop
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_init]
regex: true
- action: keep_if_equal
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port, __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number]
- source_labels:
[__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels:
[__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels:
[__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels:
[
__address__,
__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port,
]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_name
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_node
- job_name: "kubernetes-service-endpoints-slow"
scrape_interval: 5m
scrape_timeout: 30s
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- action: drop
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_init]
regex: true
- action: keep_if_equal
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port, __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number]
- source_labels:
[__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape_slow]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels:
[__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels:
[__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels:
[
__address__,
__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port,
]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_name
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_node
- job_name: "kubernetes-services"
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [http_2xx]
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
relabel_configs:
- source_labels:
[__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- target_label: __address__
replacement: blackbox
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
target_label: kubernetes_name
- job_name: "kubernetes-pods"
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- action: drop
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_init]
regex: true
- action: keep_if_equal
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port, __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number]
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels:
[__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_pod_name
- By updating
remoteWritewe’re configuring vmagent to write scraped metrics into thevminsertservice. - The second part of this yaml file is needed to add the
metric_relabel_configssection that helps us to show Kubernetes metrics on the Grafana dashboard.
Verify that vmagent’s pod is up and running by executing the following command:
kubectl get pods | grep vmagent
The expected output is:
vmagent-victoria-metrics-agent-69974b95b4-mhjph 1/1 Running 0 11m
4. Install and connect Grafana to VictoriaMetrics with Helm #
Add the Grafana Helm repository.
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
See more information on Grafana ArtifactHUB https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/grafana/grafana
To install the chart with the release name my-grafana, add the VictoriaMetrics datasource with official dashboard and the Kubernetes dashboard:
cat <<EOF | helm install my-grafana grafana/grafana -f -
datasources:
datasources.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: victoriametrics
type: prometheus
orgId: 1
url: http://vmcluster-victoria-metrics-cluster-vmselect.default.svc.cluster.local:8481/select/0/prometheus/
access: proxy
isDefault: true
updateIntervalSeconds: 10
editable: true
dashboardProviders:
dashboardproviders.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
providers:
- name: 'default'
orgId: 1
folder: ''
type: file
disableDeletion: true
editable: true
options:
path: /var/lib/grafana/dashboards/default
dashboards:
default:
victoriametrics:
gnetId: 11176
revision: 18
datasource: victoriametrics
vmagent:
gnetId: 12683
revision: 7
datasource: victoriametrics
kubernetes:
gnetId: 14205
revision: 1
datasource: victoriametrics
EOF
By running this command we:
- Install Grafana from the Helm repository.
- Provision a VictoriaMetrics data source with the url from the output above which we remembered.
- Add this dashboard for VictoriaMetrics Cluster .
- Add this dashboard for VictoriaMetrics Agent .
- Add this dashboard to see Kubernetes cluster metrics.
Please see the output log in your terminal. Copy, paste and run these commands.
The first one will show admin password for the Grafana admin.
The second and the third will forward Grafana to 127.0.0.1:3000:
kubectl get secret --namespace default my-grafana -o jsonpath="{.data.admin-password}" | base64 --decode ; echo
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=grafana,app.kubernetes.io/instance=my-grafana" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 3000
5. Check the result you obtained in your browser #
To check that VictoriaMetrics
collects metrics from k8s cluster open in browser http://127.0.0.1:3000/dashboards
and choose the Kubernetes Cluster Monitoring (via Prometheus) dashboard. Use admin for login and password that you previously got from kubectl.
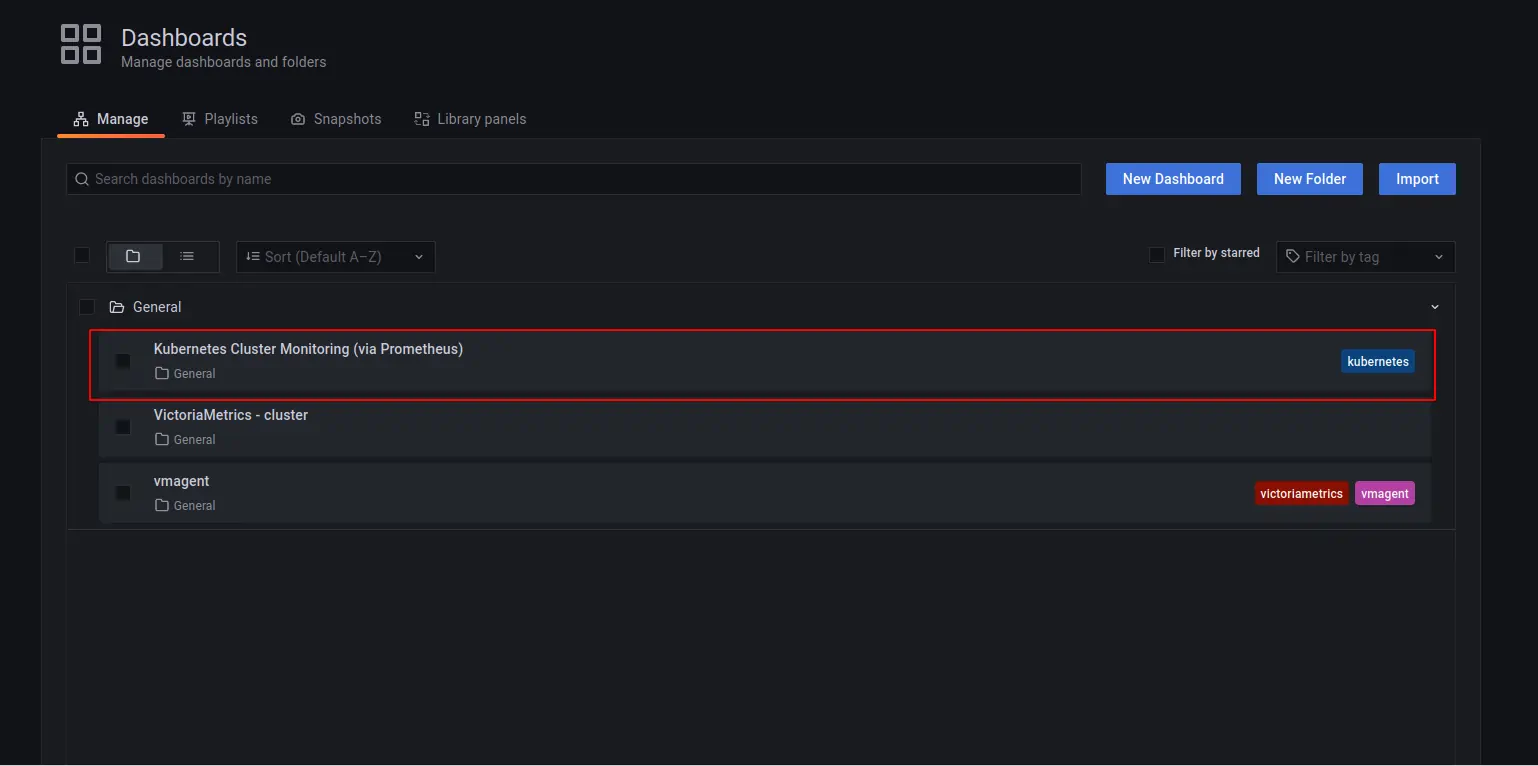
You will see something like this:
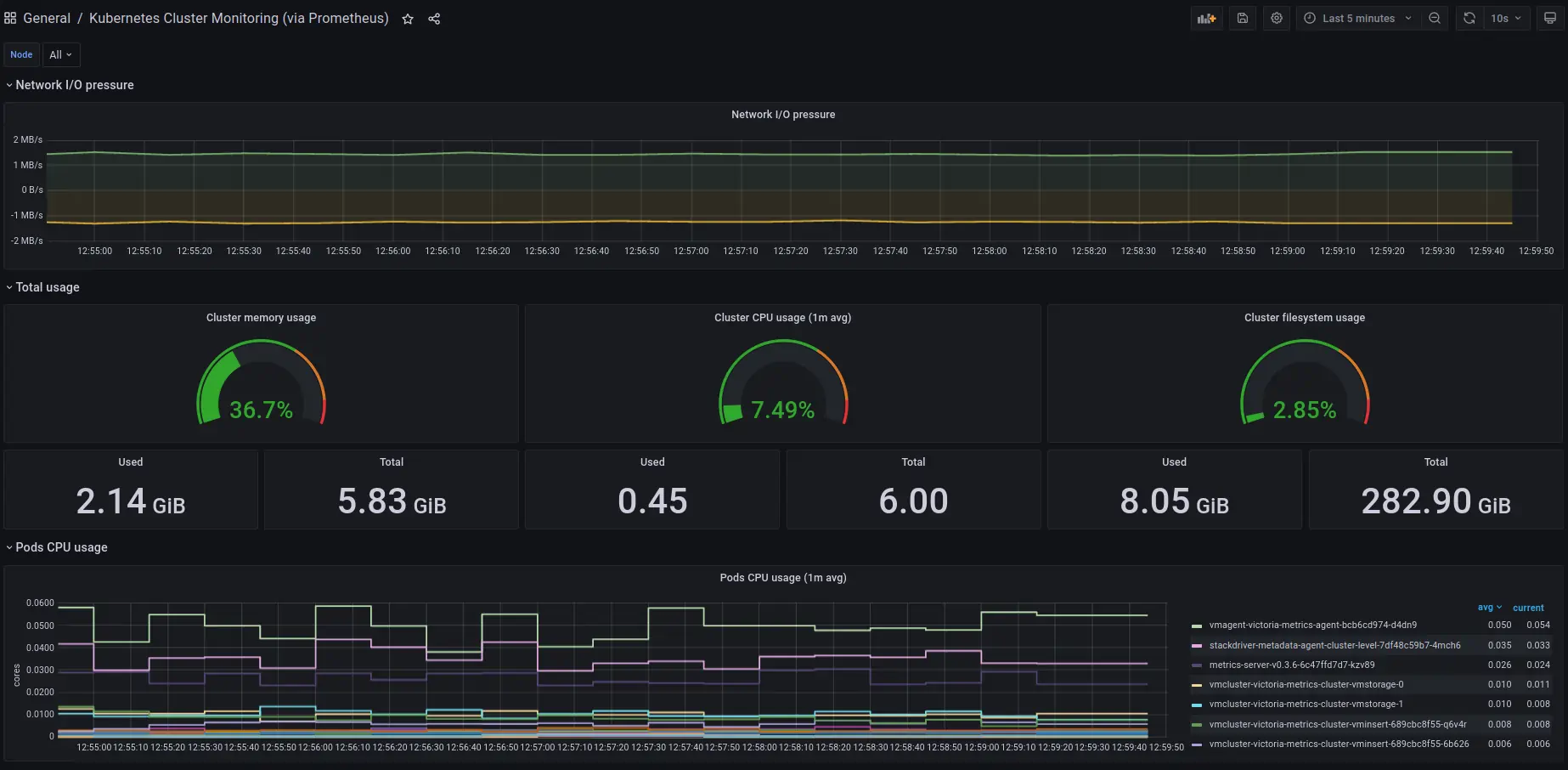
The VictoriaMetrics dashboard is also available to use:
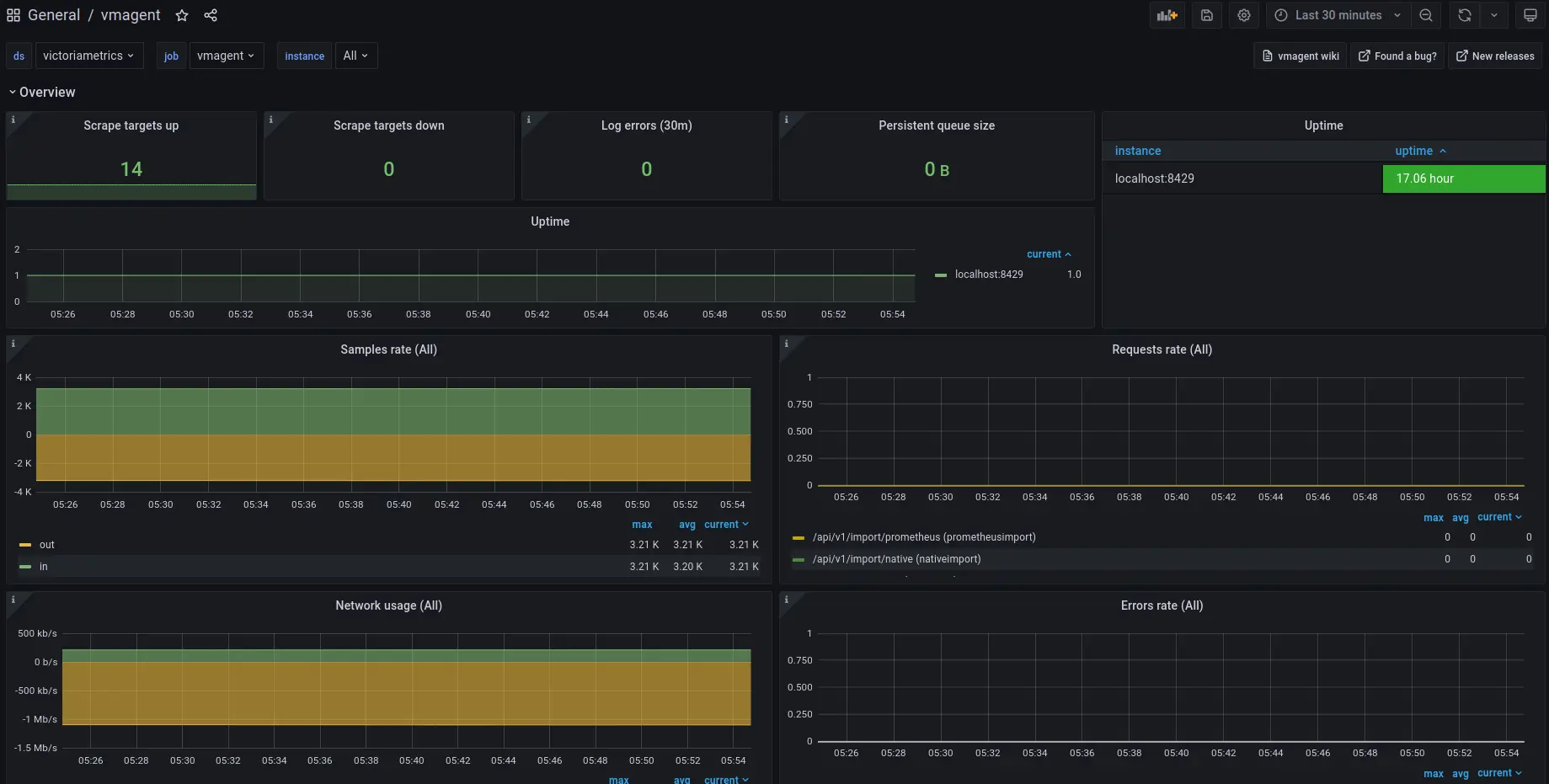
vmagent has its own dashboard:

6. Final thoughts #
- We set up TimeSeries Database for your Kubernetes cluster.
- We collected metrics from all running pods,nodes, … and stored them in a VictoriaMetrics database.
- We visualized resources used in the Kubernetes cluster by using Grafana dashboards.