VMCluster represents a high-available and fault-tolerant version of VictoriaMetrics database.
The VMCluster CRD defines a
cluster version VM
.
For each VMCluster resource, the Operator creates:
VMStorageasStatefulSet,VMSelectasStatefulSet- and
VMInsertas deployment.
For VMStorage and VMSelect headless services are created. VMInsert is created as service with clusterIP.
There is a strict order for these objects creation and reconciliation:
VMStorageis synced - the Operator waits until all its pods are ready;- Then it syncs
VMSelectwith the same manner; VMInsertis the last object to sync.
All statefulsets are created with OnDelete update type. It allows to manually manage the rolling update process for Operator by deleting pods one by one and waiting for the ready status.
Rolling update process may be configured by the operator env variables.
The most important is VM_PODWAITREADYTIMEOUT=80s - it controls how long to wait for pod’s ready status.
Specification #
You can see the full actual specification of the VMCluster resource in the API docs -> VMCluster
.
If you can’t find necessary field in the specification of the custom resource, see Extra arguments section .
Also, you can check out the examples section.
Requests Load-Balancing #
Operator provides enhanced load-balancing mechanism for vminsert and vmselect clients. By default, operator uses built-in Kubernetes service
with clusterIP type for clients connection. It’s good solution for short lived connections. But it acts poorly with long-lived TCP sessions and leads to the uneven resources utilization for vmselect and vminsert components.
Consider the following example:
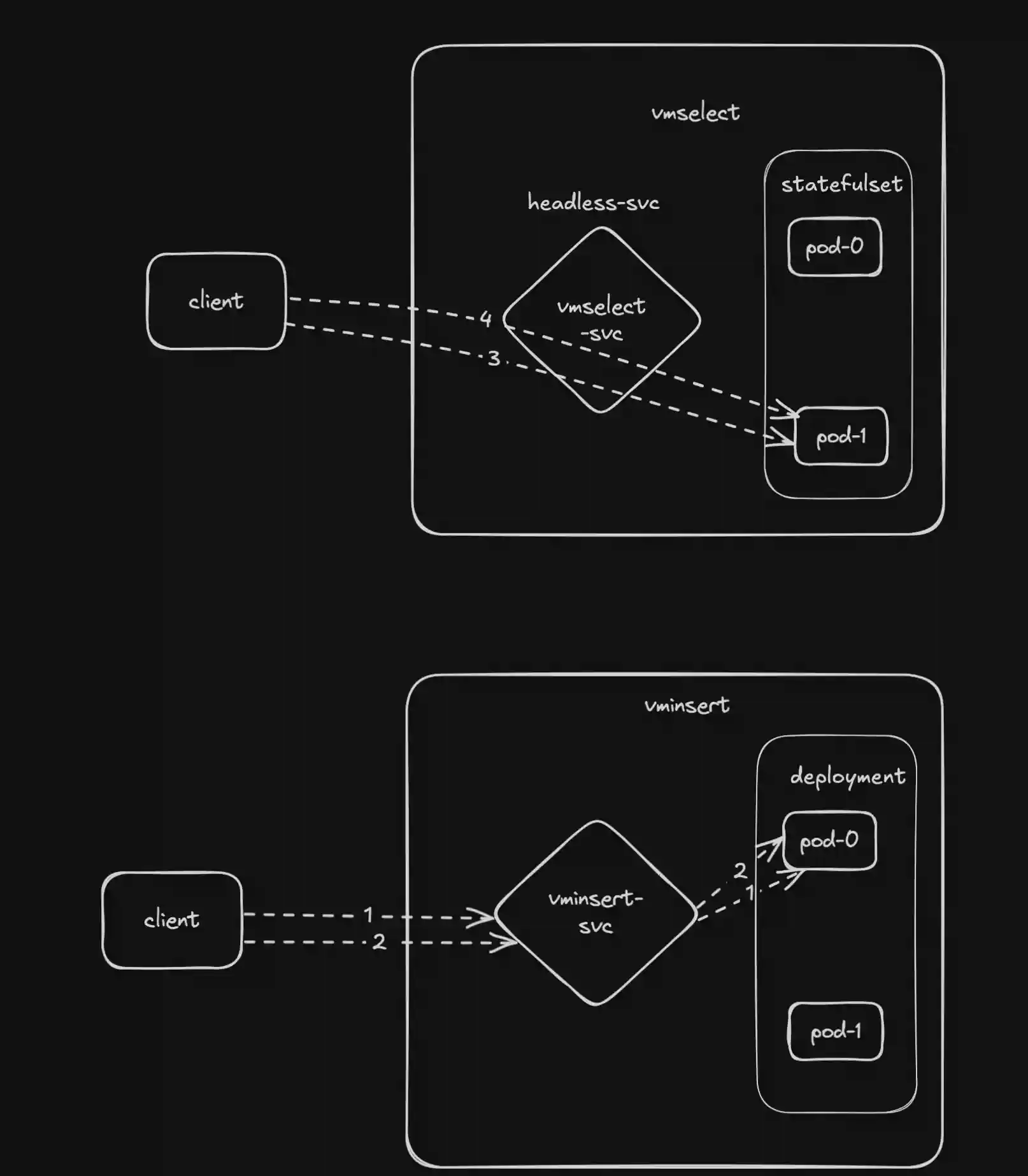
In this case clients could establish multiple connections to the same pod via service. And client requests will be served only by subset of pods.
Operator allows to tweak this behaviour with enabled requestsLoadBalancer :
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: with-balancer
spec:
retentionPeriod: "4"
replicationFactor: 1
vminsert:
replicaCount: 1
vmselect:
replicaCount: 1
vmstorage:
replicaCount: 1
requestsLoadBalancer:
enabled: true
spec:
replicaCount: 2
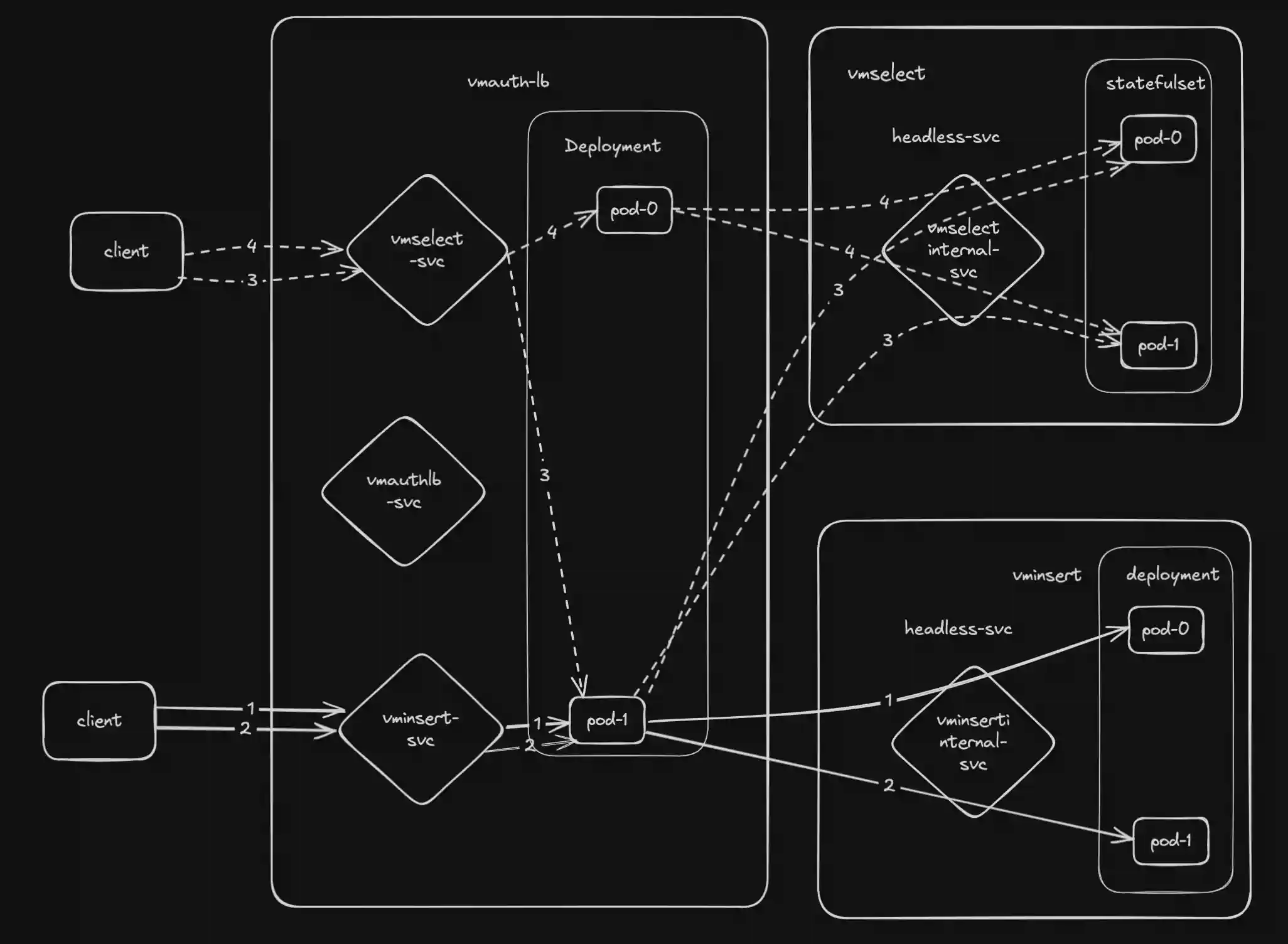
Operator will deploy VMAuth deployment with 2 replicas. And update vminsert and vmselect services to point to vmauth.
In addition, operator will create 3 additional services with the following pattern:
- vminsertinternal-CLUSTER_NAME - needed for vmselect pod discovery
- vmselectinternal-CLUSTER_NAME - needed for vminsert pod discovery
- vmclusterlb-CLUSTER_NAME - needed for metrics collection and exposing
vmselectandvminsertcomponents viaVMAuthbalancer.
Network scheme with load-balancing:
The requestsLoadBalancer feature works transparently and is managed entirely by the VMCluster operator,
with no direct access to the underlying
VMAuth
configuration.
If you need more control over load balancing behavior,
or want to combine request routing with authentication or (m)TLS,
consider deploying a standalone
VMAuth
resource instead of enabling requestsLoadBalancer.
High availability #
The cluster version provides a full set of high availability features - metrics replication, node failover, horizontal scaling.
First, we recommend familiarizing yourself with the high availability tools provided by “VictoriaMetrics Cluster” itself:
VMCluster supports all listed in the above-mentioned articles parameters and features:
replicationFactor- the number of replicas for each metric.- for every component of cluster (
vmstorage/vmselect/vminsert):replicaCount- the number of replicas for components of cluster.affinity- the affinity (the pod’s scheduling constraints) for components pods. See more details in kubernetes docs .topologySpreadConstraints- controls how pods are spread across your cluster among failure-domains such as regions, zones, nodes, and other user-defined topology domains. See more details in kubernetes docs .
In addition, operator:
- uses k8s services or vmauth for load balancing between
vminsertandvmselectcomponents, - uses health checks for to determine the readiness of components for work after restart,
- allows to horizontally scale all cluster components just by changing
replicaCountfield.
Here is an example of a VMCluster resource with HA features:
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: example-persistent
spec:
replicationFactor: 2
vmstorage:
replicaCount: 10
storageDataPath: "/vm-data"
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: "app.kubernetes.io/name"
operator: In
values:
- "vmstorage"
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
storage:
volumeClaimTemplate:
spec:
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
resources:
limits:
cpu: "2"
memory: 2048Mi
vmselect:
replicaCount: 3
cacheMountPath: "/select-cache"
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: "app.kubernetes.io/name"
operator: In
values:
- "vmselect"
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
storage:
volumeClaimTemplate:
spec:
resources:
requests:
storage: 2Gi
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: "500Mi"
vminsert:
replicaCount: 4
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: "app.kubernetes.io/name"
operator: In
values:
- "vminsert"
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: "500Mi"
Version management #
For VMCluster you can specify tag name from releases
and repository setting per cluster object:
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: example
spec:
vmstorage:
replicaCount: 2
image:
repository: victoriametrics/vmstorage
tag: v1.110.13-cluster
pullPolicy: Always
vmselect:
replicaCount: 2
image:
repository: victoriametrics/vmselect
tag: v1.110.13-cluster
pullPolicy: Always
vminsert:
replicaCount: 2
image:
repository: victoriametrics/vminsert
tag: v1.110.13-cluster
pullPolicy: Always
or for all cluster components all together, using clusterVersion property:
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: example
spec:
clusterVersion: v1.110.13-cluster
Also, you can specify imagePullSecrets if you are pulling images from private repo,
but imagePullSecrets is global setting for all VMCluster specification:
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: example
spec:
vmstorage:
replicaCount: 2
image:
repository: victoriametrics/vmstorage
tag: v1.110.13-cluster
pullPolicy: Always
vmselect:
replicaCount: 2
image:
repository: victoriametrics/vmselect
tag: v1.110.13-cluster
pullPolicy: Always
vminsert:
replicaCount: 2
image:
repository: victoriametrics/vminsert
tag: v1.110.13-cluster
pullPolicy: Always
imagePullSecrets:
- name: my-repo-secret
# ...
Resource management #
You can specify resources for each component of VMCluster resource in the spec section of the VMCluster CRD.
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: resources-example
spec:
# ...
vmstorage:
resources:
requests:
memory: "16Gi"
cpu: "4"
limits:
memory: "16Gi"
cpu: "4"
# ...
vmselect:
resources:
requests:
memory: "16Gi"
cpu: "4"
limits:
memory: "16Gi"
cpu: "4"
# ...
vminsert:
resources:
requests:
memory: "16Gi"
cpu: "4"
limits:
memory: "16Gi"
cpu: "4"
# ...
If these parameters are not specified, then,
by default all VMCluster pods have resource requests and limits from the default values of the following
operator parameters
:
VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMSTORAGEDEFAULT_RESOURCE_LIMIT_MEM- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmstoragepods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMSTORAGEDEFAULT_RESOURCE_LIMIT_CPU- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmstoragepods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMSTORAGEDEFAULT_RESOURCE_REQUEST_MEM- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmstoragepods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMSTORAGEDEFAULT_RESOURCE_REQUEST_CPU- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmstoragepods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMSELECTDEFAULT_RESOURCE_LIMIT_MEM- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmselectpods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMSELECTDEFAULT_RESOURCE_LIMIT_CPU- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmselectpods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMSELECTDEFAULT_RESOURCE_REQUEST_MEM- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmselectpods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMSELECTDEFAULT_RESOURCE_REQUEST_CPU- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmselectpods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMINSERTDEFAULT_RESOURCE_LIMIT_MEM- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmselectpods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMINSERTDEFAULT_RESOURCE_LIMIT_CPU- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmselectpods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMINSERTDEFAULT_RESOURCE_REQUEST_MEM- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmselectpods,VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_VMINSERTDEFAULT_RESOURCE_REQUEST_CPU- default memory limit forVMCluster/vmselectpods.
These default parameters will be used if:
VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_USEDEFAULTRESOURCESis set totrue(default value),VMCluster/*CR doesn’t haveresourcesfield inspecsection.
Field resources in VMCluster/* spec have higher priority than operator parameters.
If you set VM_VMCLUSTERDEFAULT_USEDEFAULTRESOURCES to false and don’t specify resources in VMCluster/* CRD,
then VMCluster/* pods will be created without resource requests and limits.
Also, you can specify requests without limits - in this case default values for limits will not be used.
Enterprise features #
VMCluster supports following features from VictoriaMetrics Enterprise :
- Downsampling
- Multiple retentions / Retention filters
- Advanced per-tenant statistic
- mTLS for cluster components
- Backup automation
VMCluster doesn’t support yet feature Automatic discovery for vmstorage nodes .
For using Enterprise version of vmcluster you need to:
- specify license at
spec.license.keyor atspec.license.keyRef. - change version of
vmclusterto version with-enterprise-clustersuffix using Version management .
Downsampling #
After that you can pass
Downsampling
flag to VMCluster/vmselect and VMCluster/vmstorage with
extraArgs
too.
Here are complete example for Downsampling :
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: ent-example
spec:
# enabling enterprise features
license:
keyRef:
name: k8s-secret-that-contains-license
key: key-in-a-secret-that-contains-license
clusterVersion: v1.110.13-enterprise-cluster
vmselect:
# enabling enterprise features for vmselect
extraArgs:
# using enterprise features: Downsampling
# more details about downsampling you can read on https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/cluster-victoriaMetrics/#downsampling
downsampling.period: 30d:5m,180d:1h,1y:6h,2y:1d
vmstorage:
# enabling enterprise features for vmstorage
extraArgs:
# using enterprise features: Downsampling
# more details about downsampling you can read on https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/cluster-victoriametrics/#downsampling
downsampling.period: 30d:5m,180d:1h,1y:6h,2y:1d
# ...other fields...
Retention filters #
You can pass
Retention filters
flag to VMCluster/vmstorage with
extraArgs
.
Here are complete example for Retention filters :
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: ent-example
spec:
# enabling enterprise features
license:
keyRef:
name: k8s-secret-that-contains-license
key: key-in-a-secret-that-contains-license
clusterVersion: v1.110.13-enterprise-cluster
vmstorage:
extraArgs:
# using enterprise features: Retention filters
# more details about retention filters you can read on https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/cluster-victoriametrics/#retention-filters
retentionFilter: '{vm_account_id="5",env="dev"}:5d,{vm_account_id="5",env="prod"}:5y'
# ...other fields...
Advanced per-tenant statistic #
For using Advanced per-tenant statistic you only need to enable Enterprise version of vmcluster components and operator will automatically create Scrape objects for cluster components.
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: ent-example
spec:
# enabling enterprise features
license:
keyRef:
name: k8s-secret-that-contains-license
key: key-in-a-secret-that-contains-license
clusterVersion: v1.110.13-enterprise-cluster
# ...other fields...
After that VMAgent will automatically scrape Advanced per-tenant statistic for cluster components.
mTLS protection #
You can pass
mTLS protection
flags to VMCluster/vmstorage, VMCluster/vmselect and VMCluster/vminsert with
extraArgs
and mount secret files
with extraVolumes and extraVolumeMounts fields.
Here are complete example for mTLS protection
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: ent-example
spec:
# enabling enterprise features
license:
keyRef:
name: k8s-secret-that-contains-license
key: key-in-a-secret-that-contains-license
clusterVersion: v1.110.13-enterprise-cluster
vmselect:
extraArgs:
# using enterprise features: mTLS protection
# more details about mTLS protection you can read on https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/cluster-victoriametrics/#mtls-protection
cluster.tls: true
cluster.tlsCAFile: /etc/mtls/ca.crt
cluster.tlsCertFile: /etc/mtls/vmselect.crt
cluster.tlsKeyFile: /etc/mtls/vmselect.key
extraVolumes:
- name: mtls
secret:
secretName: mtls
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: mtls
mountPath: /etc/mtls
vminsert:
extraArgs:
# using enterprise features: mTLS protection
# more details about mTLS protection you can read on https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/cluster-victoriametrics/#mtls-protection
cluster.tls: true
cluster.tlsCAFile: /etc/mtls/ca.crt
cluster.tlsCertFile: /etc/mtls/vminsert.crt
cluster.tlsKeyFile: /etc/mtls/vminsert.key
extraVolumes:
- name: mtls
secret:
secretName: mtls
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: mtls
mountPath: /etc/mtls
vmstorage:
extraEnvs:
- name: POD
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
extraArgs:
# using enterprise features: mTLS protection
# more details about mTLS protection you can read on https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/cluster-victoriametrics/#mtls-protection
cluster.tls: true
cluster.tlsCAFile: /etc/mtls/ca.crt
cluster.tlsCertFile: /etc/mtls/$(POD).crt
cluster.tlsKeyFile: /etc/mtls/$(POD).key
extraVolumes:
- name: mtls
secret:
secretName: mtls
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: mtls
mountPath: /etc/mtls
# ...other fields...
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mtls
namespace: default
stringData:
ca.crt: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
mtls-vmstorage-0.crt: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
mtls-vmstorage-0.key: |
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
mtls-vmstorage-1.crt: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
mtls-vmstorage-1.key: |
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
vminsert.crt: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
vminsert.key: |
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
vmselect.crt: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
vmselect.key: |
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
Example commands for generating certificates you can read on this page .
Backup automation #
You can check vmbackupmanager documentation for backup automation. It contains a description of the service and its features. This section covers vmbackumanager integration in vmoperator.
VMCluster has built-in backup configuration, it uses vmbackupmanager - proprietary tool for backups.
It supports incremental backups (hourly, daily, weekly, monthly) with popular object storages (aws s3, google cloud storage).
Here is a complete example for backup configuration:
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: ent-example
spec:
vmstorage:
vmBackup:
# this feature is only available in Victoriametrics Enterprise
# more details about backup automation you can read on https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/vmbackupmanager/
destination: "s3://your_bucket/folder"
# Read the object storage credentials from a secret
credentialsSecret:
name: remote-storage-keys
key: credentials
# customS3Endpoint: 'https://s3.example.com' # uncomment and adjust if you using s3 compatible storage instead of AWS s3
# uncomment and adjust to fit your backup schedule
# disableHourly: false
# disableDaily: false
# disableWeekly: false
# disableMonthly: false
# ...other fields...
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: remote-storage-keys
type: Opaque
stringData:
credentials: |-
[default]
aws_access_key_id = your_access_key_id
aws_secret_access_key = your_secret_access_key
NOTE: for cluster version operator adds suffix for destination: "s3://your_bucket/folder", it becomes "s3://your_bucket/folder/$(POD_NAME)".
It’s needed to make consistent backups for each storage node.
You can read more about backup configuration options and mechanics here
Possible configuration options for backup crd can be found at link
Using VMBackupmanager for restoring backups in Kubernetes environment is described here .
Also see VMCluster example spec here .
Examples #
Minimal example without persistence #
apiVersion: operator.victoriametrics.com/v1beta1
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: example-minimal
spec:
# ...
retentionPeriod: "1"
vmstorage:
replicaCount: 2
vmselect:
replicaCount: 2
vminsert:
replicaCount: 2
With persistence #
kind: VMCluster
metadata:
name: example-persistent
spec:
# ...
retentionPeriod: "4"
replicationFactor: 2
vmstorage:
replicaCount: 2
storageDataPath: "/vm-data"
storage:
volumeClaimTemplate:
spec:
storageClassName: standard
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
resources:
limits:
cpu: "0.5"
memory: 500Mi
vmselect:
replicaCount: 2
cacheMountPath: "/select-cache"
storage:
volumeClaimTemplate:
spec:
resources:
requests:
storage: 2Gi
resources:
limits:
cpu: "0.3"
memory: "300Mi"
vminsert:
replicaCount: 2