This document describes how to configure and use vmauth and VictoriaLogs components in the context of load balancing, access protection and log visibility management.
To configure secure communication between components in VictoriaLogs cluster mode, follow this documentation .
vmauth is an HTTP proxy that provides the following features:
- Load balancing across configured HTTP backends.
- Authentication via Basic Auth, Bearer tokens, or mTLS.
- Access control to specific endpoints or data paths.
- Easy to configure.
vmauth is not specifically aware of VictoriaLogs and does not offer any hidden features for tighter integration with other VictoriaMetrics components. Therefore, you can use any other HTTP proxy such as Nginx, Traefik, Envoy or HAProxy.
However, using vmauth makes it easy to configure authorization and receive community support or enterprise support from the VictoriaMetrics team if any issues arise.
For more detailed information and advanced vmauth configuration, see vmauth documentation .
All configuration examples in this documentation apply to VictoriaLogs single-node , vlselect , vlinsert and vlagent since they have the same search/write API.
Search Authorization #
For log search, both
VictoriaLogs single-node
and
vlselect
expose the same search API endpoints,
which
start with the /select/ prefix
.
When configuring request authorization or load balancing, it is important to allow access to this path prefix.
Below is an example of a vmauth configuration that:
- Uses Basic auth for request authentication.
- Authorizes access to paths starting with
/select/. - Distributes requests between two VictoriaLogs instances:
victoria-logs-1andvictoria-logs-2.
users:
- username: foo
password: bar
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/select/.*"]
url_prefix:
- http://victoria-logs-1:9428
- http://victoria-logs-2:9428
victoria-logs-1 and victoria-logs-2 can be either two VictoriaLogs single-node instances with replicated data according to
these docs
,
or vlselect instances in the
VictoriaLogs cluster
.
Enumerate all the vlselect instances in the cluster under the url_prefix config above in order to spread load among all the available vlselect instances.
The diagram below illustrates this architecture in the clustered version of VictoriaLogs:
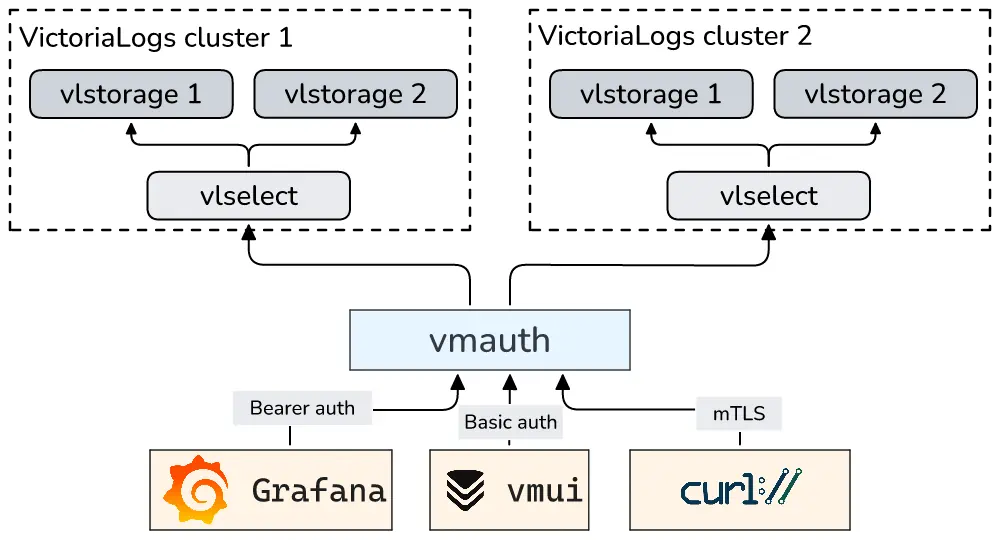
Update the connection settings in all clients (like Grafana) after configuring the vmauth in order
to match the selected authentication method and the vmauth endpoint.
Important: Requests sent directly to VictoriaLogs bypass vmauth and are not authorized.
To ensure security, it is strongly recommended to restrict network access to VictoriaLogs and prevent direct access from unauthorized clients.
It is recommended to pass the -insert.disable command-line flag to vlselect to disable the write API.
This helps protect against accidental data ingestion via vlselect in case of improperly configured log shippers.
For configuration examples using Bearer tokens, Basic auth, and mTLS, see vmauth/Authorization .
Cluster routing #
vmauth allows selecting different clusters depending on the request path. For example:
unauthorized_user:
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/cold/select/.*"]
url_prefix: http://victoria-logs-cold:9428
# drop /cold/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 1
- src_paths: ["/hot/select/.*"]
url_prefix: http://victoria-logs-hot:9428
# drop /hot/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 1
The configuration above enables proxying all requests that start with the path prefix /cold/select/ to the backend at http://victoria-logs-cold:9428,
and requests with the path prefix /hot/select/ to the backend located at http://victoria-logs-hot:9428.
This approach is useful when applying different retention policies for various types of logs. For example, you might store warn-level and higher severity logs in the cold instance/cluster with longer retention, while keeping debug-level and higher severity logs only in the hot instance/cluster with shorter retention.
The drop_src_path_prefix_parts parameter is used to remove the prefix from the path when proxying the request to VictoriaLogs.
For example, if vmauth receives a request to /cold/select/logsql/query,
VictoriaLogs will receive the path without the /cold/ prefix, allowing it to properly handle the search query.
Tenant-based request proxying #
The following vmauth config proxies /select/* requests with the AccountID: 0 HTTP header
to the long-term VictoriaLogs instance or cluster, while requests with the AccountID: 1 HTTP header
are proxied to the short-term VictoriaLogs instance or cluster.
unauthorized_user:
url_map:
# Proxy requests for the given tenant (AccountID=0) to long-term VictoriaLogs
# and override the ProjectID with 0.
- src_paths: ["/select/.*"]
src_headers:
- "AccountID: 0"
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs-longterm:9428"
headers:
- "ProjectID: 0"
# Proxy requests for the given tenant (AccountID=1) to short-term VictoriaLogs
# and override the AccountID with 0.
- src_paths: ["/select/.*"]
src_headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs-shortterm:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 0"
See also tenant-based data ingestion request proxying .
This allows building a VictoriaLogs storage system with distinct per-tenant retention configs similar to this one .
Proxying requests to the given tenants #
To properly separate and access data across tenants, two headers must be set when writing logs: AccountID and ProjectID according to
these docs
.
When querying logs, you must provide the same headers to retrieve the corresponding data.
You can use vmauth to enforce tenant-level access control by automatically setting the required headers after successful authentication.
For example, the vmauth configuration below overrides tenant headers before proxying requests to VictoriaLogs for user foo upon successful authentication:
users:
- username: foo
password: bar
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/select/.*"]
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 2"
- "ProjectID: 4"
If the user sets the AccountID or ProjectID headers themselves,
for example through vmui or Grafana data source settings, they will be overridden.
A more practical example: if you have many tenants and want to separate them by name, vmauth configuration might look like this:
users:
- username: foo
password: bar
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/my-account/kubernetes-logs/select/.*"]
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
- "ProjectID: 5"
# drop /my-account/kubernetes-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 2
- src_paths: ["/my-account/mobile-logs/select/.*"]
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
- "ProjectID: 6"
# drop /my-account/mobile-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 2
- src_paths: ["/my-account/frontend-logs/select/.*"]
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
- "ProjectID: 7"
# drop /my-account/frontend-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 2
- username: admin
password: secret
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/select/.*"]
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs:9428"
This configuration allows user foo to access 3 different tenants, and user admin to access all tenants.
However, user admin needs to set the required AccountID or ProjectID headers themselves, because vmauth will not set them.
In Grafana, you need to create a separate data source for each tenant and user, an example of such an address is: http://vmauth:8427/my-account/mobile-logs.
Using the configuration above, you do not need to set the tenant in the data source settings because vmauth will set it.
Each tenant will have vmui at the address /select/vmui/, for example: http://vmauth:8427/my-account/mobile-logs/select/vmui/.
If you want to restrict users by only one of the fields AccountID or ProjectID,
it is enough to not specify the corresponding field in the headers section.
For example, the following configuration allows user my-account-admin to have access to all ProjectIDs, but only for one AccountID:
users:
- username: my-account-admin
password: foobar
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/my-account/select/.*"]
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
# drop /my-account/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 1
To allow unauthenticated access to a specific tenant, define the unauthorized_user as shown below:
unauthorized_user:
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/my-account/frontend-logs/select/.*"]
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
- "ProjectID: 7"
# drop /my-account/frontend-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 2
This will grant all users access to logs for the specified tenant without additional authentication.
Note that if you don’t specify the AccountID or ProjectID header,
VictoriaLogs will assume that the corresponding header has a value of 0.
Access control inside a single tenant #
VictoriaLogs can apply extra filters for each request to the select APIs according to
these docs
.
This is useful when you need to give access to a subset of data within a single tenant.
If you want to hide a subset of data within a tenant, use the HTTP query parameter extra_filters.
extra_filters are enforced globally - they are propagated into all the subqueries inside the provided query. This makes it impossible to bypass the restrictions via join, union, in(<query>) and other subqueries.
Consider the example below:
users:
- username: foo
password: bar
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/select/.*"]
url_prefix:
- http://victoria-logs-1:9428?extra_filters=password:''
- http://victoria-logs-2:9428?extra_filters=password:''
With this configuration, vmauth will add the
empty filter
password:'' to each request, which means that the password field must be empty or missing in the log.
This is useful in cases when sensitive information has leaked and needs to be hidden.
To restrict log visibility within a specific
log stream
, use the extra_stream_filters query parameter.
The configuration below adds an additional
stream filter
to each request based on the request path, and routes /audit-logs to a separate VictoriaLogs instance:
users:
- username: frontend-logs-viewer
password: secret
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/frontend-logs/select/.*"]
url_prefix: http://victoria-logs:9428?extra_stream_filters=_stream%3A%7Bservice%3Dfrontend-logs%7D
# drop /frontend-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 1
- username: mobile-logs-viewer
password: secret
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/mobile-logs/select/.*"]
url_prefix: http://victoria-logs:9428?extra_stream_filters=_stream%3A%7Bservice%3Dmobile-logs%7D
# drop /mobile-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 1
- username: audit-logs-viewer
password: secret
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/audit-logs/select/.*"]
url_prefix: http://victoria-logs-audit:9428
# drop /audit-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 1
extra_filters and extra_stream_filters should be percent-encoded
when they include characters that are not URL-safe.
For example, the query _stream:{service=frontend-logs} should be written as _stream%3A%7Bservice%3Dfrontend-logs%7D.
Prefer using extra_stream_filters over extra_filters whenever possible.
This can improve search query performance because VictoriaLogs
processes searches using stream filters faster than regular filters. See
LogsQL performance optimization tips
.
Write Authorization #
For log writing,
VictoriaLogs single-node
and
vlinsert
expose the same write API endpoints
which
start with the /insert/ prefix
,
so when configuring write requests, it is important to set this path for request authorization.
Example vmauth configuration that allows insert requests
with Basic auth and distributes load between vlinsert nodes in the cluster:
users:
- username: foo
password: bar
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/insert/.*"]
url_prefix:
- "http://vlinsert-1:9428"
- "http://vlinsert-2:9428"
- "http://vlinsert-3:9428"
Note that vmauth cannot replicate data to multiple destinations - it spreads incoming requests among the configured backends. Use vlagent for replicating the data to multiple VictoriaLogs instances or multiple VictoriaLogs clusters.
If you trust the writing side, for example when collecting logs within your own cluster, you can set the query parameters and tenant headers directly on the log shipper side without an extra proxy. In such cases, it’s usually sufficient to restrict network access so only trusted agents can write to VictoriaLogs.
On the other hand, if you do not trust the writing side, for example, if the logs come from frontend or mobile apps, it is very important to secure the write API:
- Set up a secure HTTPS connection for vmauth (see these docs ) and VictoriaLogs (see these docs ).
- Protect vmauth with anti-DDoS services if needed.
- Consider the max_concurrent_requests parameter to control the number of concurrent write requests.
- Add monitoring and alerting for vmauth to control the load.
- Write logs from untrusted applications to dedicated VictoriaLogs instances or clusters so that the unpredictable write load does not affect other instances.
It is recommended to pass the -select.disable command-line flag to vlinsert in order to disable the search API.
This will secure access to the stored logs in case an attacker has direct network access to vlinsert.
For configuration examples using Bearer tokens, Basic auth, and mTLS, see these docs .
Tenant assignment #
vmauth allows redirecting requests to different tenants based on the request path.
Example vmauth configuration that allows insert requests
with Basic auth and distributes load between the configured vlinsert nodes for three different
tenants
:
users:
- username: kubernetes
password: secret
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/my-account/kubernetes-logs/insert/.*"]
url_prefix:
- "http://vlinsert-1:9428"
- "http://vlinsert-2:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
- "ProjectID: 5"
# drop /my-account/kubernetes-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 2
max_concurrent_requests: 10
- username: mobile
password: secret
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/my-account/mobile-logs/insert/.*"]
url_prefix:
- "http://vlinsert-1:9428"
- "http://vlinsert-2:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
- "ProjectID: 6"
# drop /my-account/mobile-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 2
max_concurrent_requests: 10
- username: frontend
password: secret
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/my-account/frontend-logs/insert/.*"]
url_prefix:
- "http://vlinsert-1:9428"
- "http://vlinsert-2:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
- "ProjectID: 7"
# drop /my-account/frontend-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 2
max_concurrent_requests: 10
Below is a diagram of this architecture for the clustered version of VictoriaLogs:
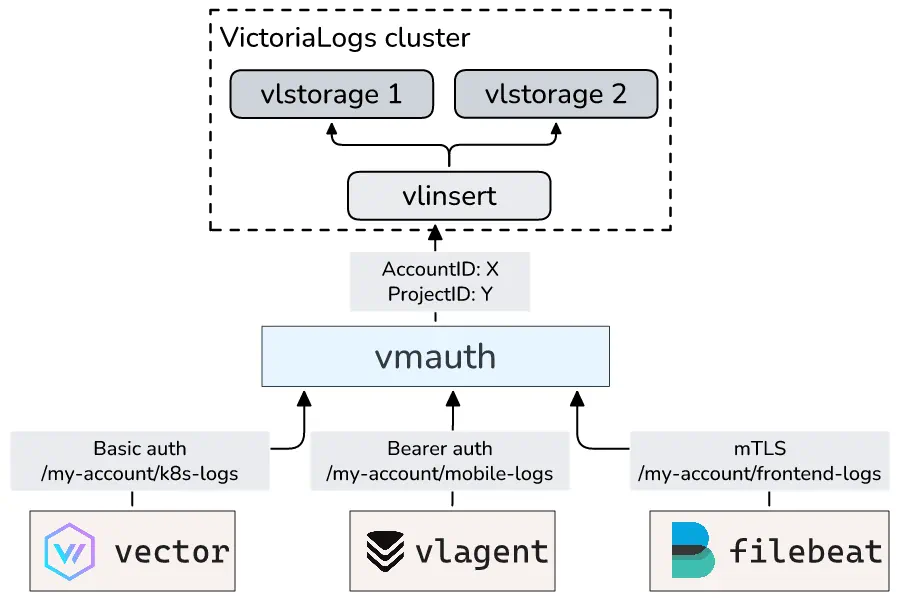
Tenant-based proxying of data ingestion requests #
The following vmauth config proxies data ingestion requests with the AccountID: 0 HTTP header
to the long-term VictoriaLogs instance or cluster, while data ingestion requests with the AccountID: 1 HTTP header
are proxied to the short-term VictoriaLogs instance or cluster:
unauthorized_user:
url_map:
# Proxy data ingestion requests for the given tenant (AccountID=0) to long-term VictoriaLogs
# and override the ProjectID with 0.
- src_paths: ["/insert/.*"]
src_headers:
- "AccountID: 0"
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs-longterm:9428"
headers:
- "ProjectID: 0"
# Proxy data ingestion requests for the given tenant (AccountID=1) to short-term VictoriaLogs
# and override the AccountID with 0.
- src_paths: ["/insert/.*"]
src_headers:
- "AccountID: 1"
url_prefix: "http://victoria-logs-shortterm:9428"
headers:
- "AccountID: 0"
This allows building a VictoriaLogs storage system with distinct per-tenant retention configs similar to this one .
Adding extra fields #
You can use the extra_fields parameter in vmauth to automatically add fields to incoming log entries according to
these docs
.
This is helpful when the writing side cannot include certain metadata, such as the source service name.
The example below adds a service field with the value frontend-logs to all the logs received at the /frontend-logs/insert/* path.
It also includes the _stream_fields parameter as an example of how to configure
stream
for such logs.
users:
- bearer_token: foobar
url_map:
- src_paths: ["/frontend-logs/insert/.*"]
url_prefix:
- "http://vlinsert-1:9428?extra_fields=service=frontend-logs&_stream_fields=service"
- "http://vlinsert-2:9428?extra_fields=service=frontend-logs&_stream_fields=service"
- "http://vlinsert-3:9428?extra_fields=service=frontend-logs&_stream_fields=service"
# drop /frontend-logs/ path prefix from the original request before proxying it to url_prefix.
drop_src_path_prefix_parts: 1
max_concurrent_requests: 10
Any field sent by the application will be overridden by the value set in the extra_fields, if defined.
This prevents the log shipper from unexpectedly overriding the provided extra_fields.