VictoriaTraces is an open-source, user-friendly database designed for storing and querying distributed tracing data , built by the VictoriaMetrics team.
Prominent features #
VictoriaTraces provides the following prominent features:
- It is resource-efficient and fast. It uses up to 3.7x less RAM and up to 2.6x less CPU than other solutions such as Grafana Tempo.
- VictoriaTraces’ capacity and performance scales linearly with the available resources (CPU, RAM, disk IO, disk space). Also, it can scale horizontally to many nodes in cluster mode .
- It has no additional storage dependencies (such as object storage or external databases like ClickHouse and Elasticsearch) for production readiness.
- It accepts trace spans in the popular OpenTelemetry protocol (OTLP).
- It provides Jaeger Query Service JSON APIs to integrate with Grafana or Jaeger Frontend .
- It supports alerting - see these docs .
If you want to play with the VictoriaTraces demo, simply go to our Grafana playground to query and visualize the traces, and visit the VictoriaTraces playground to see how trace spans are structured and stored.
Operation #
Install #
To quickly try VictoriaTraces, just download the VictoriaTraces executable or docker image from Docker Hub or Quay and start it with the desired command-line flags. See also QuickStart guide for additional information.
How to build from sources #
Building from sources is reasonable when developing additional features specific to your needs or when testing bugfixes.
How to build from sources
Clone VictoriaTraces repository:
git clone https://github.com/VictoriaMetrics/VictoriaTraces.git;
cd VictoriaTraces;
Build binary with go build #
- Install Go .
- Run
make victoria-tracesfrom the root folder of the repository . It buildsvictoria-tracesbinary and puts it into thebinfolder.
Build binary with Docker #
- Install docker .
- Run
make victoria-traces-prodfrom the root folder of the repository . It buildsvictoria-traces-prodbinary and puts it into thebinfolder.
Building docker images #
Run make package-victoria-traces. It builds victoriametrics/victoria-traces:<PKG_TAG> docker image locally.
<PKG_TAG> is auto-generated image tag, which depends on source code in the repository.
The <PKG_TAG> may be manually set via PKG_TAG=foobar make package-victoria-traces.
The base docker image is alpine
but it is possible to use any other base image
by setting it via <ROOT_IMAGE> environment variable.
For example, the following command builds the image on top of scratch
image:
ROOT_IMAGE=scratch make package-victoria-traces
Configure VictoriaTraces #
VictoriaTraces is configured via command-line flags. All the command-line flags have sane defaults, so there is no need in tuning them in general case. VictoriaTraces runs smoothly in most environments without additional configuration.
Pass -help to VictoriaTraces in order to see the list of supported command-line flags with their description and default values:
/path/to/victoria-traces -help
The following command-line flags are used the most:
-storageDataPath- VictoriaTraces stores all the data in this directory. The default path isvictoria-traces-datain the current working directory.-retentionPeriod- retention for stored data. Older data is automatically deleted. Default retention is 7 days.
You can find the list of the command-line flags .
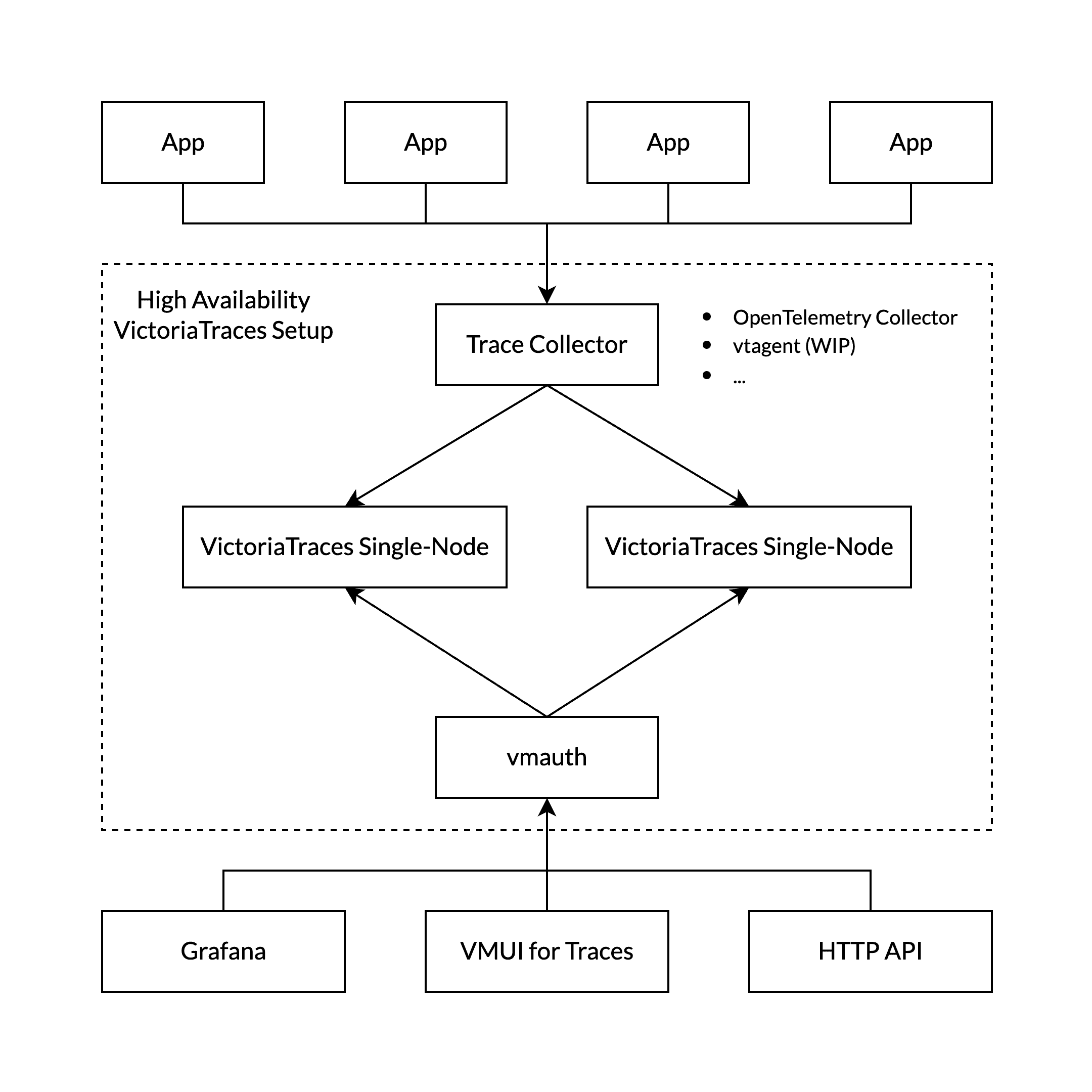
High Availability #
High Availability (HA) Setup with VictoriaTraces Single-Node Instances #
This schema outlines how to configure a High Availability (HA) setup using VictoriaTraces Single-Node instances. The setup consists of the following components:
Trace Collector: The trace collector should support multiplexing incoming data to multiple outputs (destinations). Popular trace collector like the OpenTelemetry collector already offer this capability. Refer to their documentation for configuration details.
VictoriaTraces Single-Node Instances: Use two or more instances to achieve HA.
vmauth or Load Balancer: Used for reading data from one of the replicas to ensure balanced and redundant access.
Monitoring #
VictoriaTraces exposes internal metrics in Prometheus exposition format at http://<victoria-traces>:10428/metrics page.
It is recommended to set up monitoring of these metrics via VictoriaMetrics
(see
these docs
),
vmagent (see
these docs
) or via Prometheus.
We recommend installing Grafana dashboard for VictoriaTraces single-node or cluster .
We recommend setting up alerts via vmalert or via Prometheus.
VictoriaTraces emits its own logs to stdout. It is recommended to investigate these logs during troubleshooting.
Backup and restore #
VictoriaTraces stores data into independent per-day partitions. Every partition is stored in a distinct directory under <-storageDataPath>/partitions/ directory.
It is safe to create a backup of separate partitions with the rsync
command.
The files in VictoriaTraces have the following properties:
- All the data files are immutable. Small metadata files can be modified.
- Old data files are periodically merged into new data files.
Therefore, for a complete backup of some per-day partition or a set of partitions, you need to run the rsync command twice.
# example of rsync to remote host
rsync -avh --progress --delete <path-to-victoriatraces-data> <username>@<host>:<path-to-victoriatraces-backup>
The --delete option is required in the command above, since it ensures that the backup contains the full copy of the original data and doesn’t contain superfluous files.
The first rsync will sync the majority of the data, which can be time-consuming.
As VictoriaTraces continues to run, new data is ingested, potentially creating new data files and modifying metadata files.
The second rsync requires a brief detaching of the backed up partitions to ensure all data and metadata files are consistent and are no longer changing.
See
how to detach and attach partitions without the need to stop VictoriaTraces
.
This rsync will cover any changes that have occurred since the last rsync and should not take a significant amount of time.
To restore from a backup, simply rsync the backup from a remote location to the original partition directories and then
attach them
without the need to restart VictoriaTraces. Another option is to rsync the partitions from the backup while VictoriaTraces isn’t running and then start VictoriaTraces.
It will automatically discover and open all the partitions under the <-storageDataPath>/partitions/ directory.
# example of rsync from remote backup to local
rsync -avh --progress --delete <username>@<host>:<path-to-victoriatraces-backup> <path-to-victoriatraces-data>
The --delete option is required in the command above, since it ensures that the destination folder contains the full copy of the backup and doesn’t contain superfluous files.
It is also possible to use the disk snapshot in order to perform a backup. This feature could be provided by your operating system, cloud provider, or third-party tools. Note that the snapshot must be consistent to ensure reliable backup.
Retention #
By default, VictoriaTraces stores trace data with timestamps in the time range [now-7d, now], while dropping data outside the given time range.
E.g. it uses the retention of 7 days. The retention can be configured with -retentionPeriod command-line flag.
This flag accepts values starting from 1d (one day) up to 100y (100 years). See these docs
for the supported duration formats.
For example, the following command starts VictoriaTraces with the retention of 8 weeks:
/path/to/victoria-traces -retentionPeriod=8w
See also retention by disk space usage .
VictoriaTraces stores the ingested trace spans in per-day partition directories. It automatically drops partition directories outside the configured retention.
VictoriaTraces automatically drops trace spans at
data ingestion
stage
if they have timestamps outside the configured retention. A sample of dropped spans is logged with WARN message in order to simplify troubleshooting.
The vt_rows_dropped_total
metric
is incremented each time an ingested span is dropped because of timestamp outside the retention.
It is recommended to set up the following alerting rule at
vmalert
in order to be notified
when spans with wrong timestamps are ingested into VictoriaTraces:
rate(vt_rows_dropped_total[5m]) > 0
By default, VictoriaTraces doesn’t accept trace spans with timestamps bigger than now+2d, e.g. 2 days in the future.
If you need accepting trace spans with bigger timestamps, then specify the desired “future retention” via -futureRetention command-line flag.
This flag accepts values starting from 1d. See these docs
for the supported duration formats.
For example, the following command starts VictoriaTraces, which accepts trace spans with timestamps up to a year in the future:
/path/to/victoria-traces -futureRetention=1y
Retention by disk space usage #
VictoriaTraces can be configured to automatically drop older per-day partitions based on disk space usage using one of two approaches:
Absolute disk space limit #
Use the -retention.maxDiskSpaceUsageBytes command-line flag to set a fixed threshold. VictoriaTraces will drop old per-day partitions
if the total size of data at
-storageDataPath directory
becomes bigger than the specified limit.
For example, the following command starts VictoriaTraces, which drops old per-day partitions if the total
storage
size becomes bigger than 100GiB:
/path/to/victoria-traces -retention.maxDiskSpaceUsageBytes=100GiB
Percentage-based disk space limit #
Use the -retention.maxDiskUsagePercent command-line flag to set a dynamic threshold based on the filesystem’s total capacity.
VictoriaTraces will drop old per-day partitions if the filesystem containing the
-storageDataPath directory
exceeds the specified percentage usage.
For example, the following command starts VictoriaTraces, which drops old per-day partitions if the filesystem usage exceeds 80%:
/path/to/victoria-traces -retention.maxDiskUsagePercent=80
This approach is particularly useful in environments where the total disk capacity may vary (e.g., cloud environments with resizable volumes) or when you want to maintain a consistent percentage of free space regardless of the total disk size.
Important: The -retention.maxDiskSpaceUsageBytes and -retention.maxDiskUsagePercent flags are mutually exclusive.
VictoriaTraces will refuse to start if both flags are set simultaneously.
VictoriaTraces usually compresses trace spans by 10x or more times. This means that VictoriaTraces can store more than a terabyte of uncompressed
trace spans when it runs with -retention.maxDiskSpaceUsageBytes=100GiB or when using percentage-based retention on a large filesystem.
VictoriaTraces keeps at least two last days of data in order to guarantee that the traces for the last day can be returned in queries. This means that the total disk space usage may exceed the configured threshold if the size of the last two days of data exceeds the limit.
The
-retentionPeriod
is applied independently to the disk space usage limits. This means that
VictoriaTraces automatically drops trace spans older than 7 days by default if only a disk space usage flag is set.
Set the -retentionPeriod to some big value (e.g. 100y - 100 years) if trace spans shouldn’t be dropped because of time-based retention.
For example:
/path/to/victoria-traces -retention.maxDiskSpaceUsageBytes=10TiB -retentionPeriod=100y
or
/path/to/victoria-traces -retention.maxDiskUsagePercent=85 -retentionPeriod=100y
Storage #
VictoriaTraces stores all its data in a single directory - victoria-traces-data. The path to the directory can be changed via -storageDataPath command-line flag.
For example, the following command starts VictoriaTraces, which stores the data at /var/lib/victoria-traces:
/path/to/victoria-traces -storageDataPath=/var/lib/victoria-traces
VictoriaTraces automatically creates the -storageDataPath directory on the first run if it is missing. VictoriaTraces stores trace spans
per every day into a separated subdirectory (aka per-day partition). See
partitions lifecycle
for details.
VictoriaTraces switches to cluster mode if -storageNode command-line flag is specified:
- It stops storing the ingested trace spans locally in cluster mode. It spreads them evenly among
vtstoragenodes specified via the-storageNodecommand-line flag. - It stops querying the locally stored trace spans in cluster mode. It queries
vtstoragenodes specified via-storageNodecommand-line flag.
See cluster mode docs for details.
Partitions lifecycle #
The ingested data is stored in per-day subdirectories (partitions) at the <-storageDataPath>/partitions/ directory. The per-day subdirectories have YYYYMMDD names.
For example, the directory with the name 20250418 contains data with
_time field
values
at April 18, 2025 UTC. This allows flexible data management.
For example, old per-day data is automatically and quickly deleted according to the provided retention policy by removing the corresponding per-day subdirectory (partition).
VictoriaTraces supports dynamic attach and detach of per-day partitions, by using the following HTTP API endpoints:
/internal/partition/attach?name=YYYYMMDD- attaches the partition directory with the given nameYYYYMMDDto VictoriaTraces, so it becomes visible for querying and can be used for data ingestion. The directory must be placed inside<-storageDataPath>/partitionsand it must contain valid data for the givenYYYYMMDDday./internal/partition/detach?name=YYYYMMDD- detaches the partition directory with the given nameYYYYMMDDfrom VictoriaTraces, so it is no longer visible for querying and cannot be used for data ingestion. The/internal/partition/detachendpoint waits until all the concurrently executed queries stop reading the data from the detached partition before returning. This allows safe manipulation of the detached partitions by external tools on disk after returning from the/internal/partition/detachendpoint.
These endpoints can be protected from unauthorized access via -partitionManageAuthKey
command-line flag
.
These endpoints can be used for building a flexible per-partition backup / restore schemes as described in these docs .
These endpoints can be used also for setting up automated multi-tier storage schemes where recently ingested data is stored to VictoriaTraces instances with fast NVMe (SSD) disks, while historical data is gradually migrated to VictoriaTraces instances with slower, but bigger and less expensive HDD disks. This scheme can be implemented with the following simple cron job, which must run once per day:
- To copy per-day partition for the older day stored at NVMe from NVMe to HDD, with the help of
rsync. - To detach the copied partition from the VictoriaTraces with NVMe.
- To run the
rsyncon the copied partition again in order sync the possible changes in the partition during the previous copy. - To attach the copied partition to the VictoriaTraces with HDD.
- To delete the copied partition directory from the VictoriaTraces with NVMe.
All the VictoriaTraces with NVMe and HDD disks can be queried simultaneously via vtselect component of VictoriaTraces cluster,
since single-node VictoriaTraces instances can be a part of cluster.
How does it work #
VictoriaTraces was initially built on top of VictoriaLogs , a log database. It receives trace spans in OTLP format, transforms them into structured logs, and provides Jaeger Query Service JSON APIs for querying.
For detailed data model and example, see: Key Concepts .
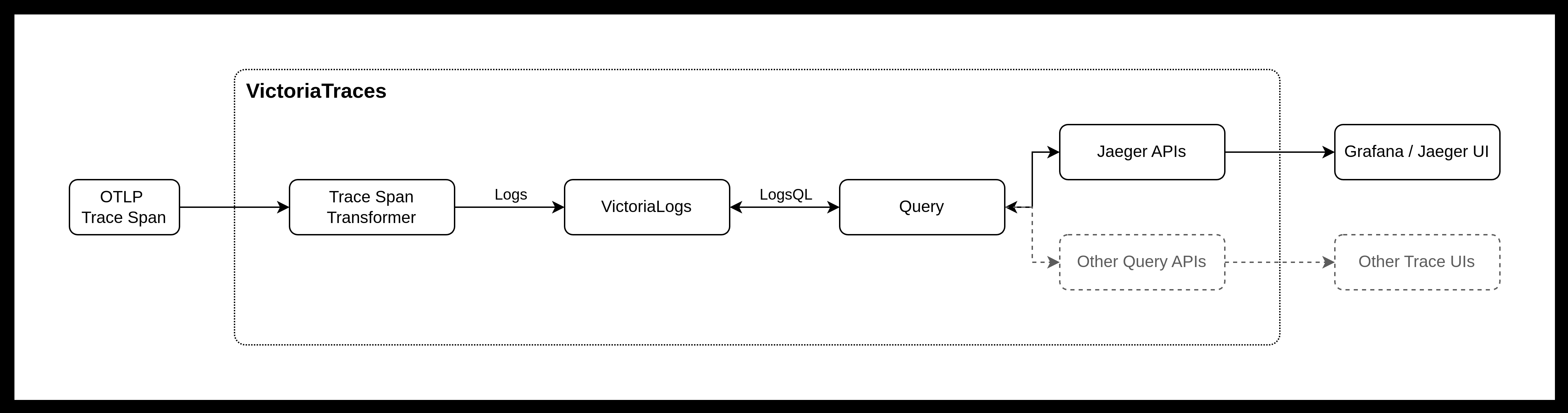
Building VictoriaTraces in this way enables it to scale easily and linearly with the available resources, like VictoriaLogs.
Multitenancy #
VictoriaTraces supports multitenancy. A tenant is identified by (AccountID, ProjectID) pair, where AccountID and ProjectID are arbitrary 32-bit unsigned integers.
The AccountID and ProjectID fields can be set during
data ingestion
and
querying
via AccountID and ProjectID request headers.
If AccountID and/or ProjectID request headers aren’t set, then the default 0 value is used.
VictoriaTraces has very low overhead for per-tenant management, so it is OK to have thousands of tenants in a single VictoriaTraces instance.
VictoriaTraces doesn’t perform per-tenant authorization. Use vmauth or similar tools for per-tenant authorization.
Security #
It is expected that VictoriaTraces runs in a protected environment, which is unreachable from the internet without proper authorization. It is recommended providing access to VictoriaTraces data ingestion APIs and querying APIs via vmauth or similar authorization proxies.
It is recommended protecting internal HTTP endpoints from unauthorized access:
/internal/force_flush- via-forceFlushAuthKeycommand-line flag ./internal/force_merge- via-forceMergeAuthKeycommand-line flag ./internal/partition/*- via-partitionManageAuthKeycommand-line flag .
List of command-line flags #
-blockcache.missesBeforeCaching int
The number of cache misses before putting the block into cache. Higher values may reduce indexdb/dataBlocks cache size at the cost of higher CPU and disk read usage (default 2)
-defaultMsgValue string
Default value for _msg field; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victorialogs/keyconcepts/#message-field (default "-")
-defaultParallelReaders int
Default number of parallel data readers to use for executing every query; higher number of readers may help increasing query performance on high-latency storage such as NFS or S3 at the cost of higher RAM usage; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victorialogs/logsql/#parallel_readers-query-option (default 16)
-delete.enable
Whether to enable /delete/* HTTP endpoints
-enableTCP6
Whether to enable IPv6 for listening and dialing. By default, only IPv4 TCP and UDP are used
-envflag.enable
Whether to enable reading flags from environment variables in addition to the command line. Command line flag values have priority over values from environment vars. Flags are read only from the command line if this flag isn't set. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/single-server-victoriametrics/#environment-variables for more details
-envflag.prefix string
Prefix for environment variables if -envflag.enable is set
-filestream.disableFadvise
Whether to disable fadvise() syscall when reading large data files. The fadvise() syscall prevents from eviction of recently accessed data from OS page cache during background merges and backups. In some rare cases it is better to disable the syscall if it uses too much CPU
-flagsAuthKey value
Auth key for /flags endpoint. It must be passed via authKey query arg. It overrides -httpAuth.*
Flag value can be read from the given file when using -flagsAuthKey=file:///abs/path/to/file or -flagsAuthKey=file://./relative/path/to/file.
Flag value can be read from the given http/https url when using -flagsAuthKey=http://host/path or -flagsAuthKey=https://host/path
-forceFlushAuthKey value
authKey, which must be passed in query string to /internal/force_flush . It overrides -httpAuth.* . See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/#forced-flush
Flag value can be read from the given file when using -forceFlushAuthKey=file:///abs/path/to/file or -forceFlushAuthKey=file://./relative/path/to/file.
Flag value can be read from the given http/https url when using -forceFlushAuthKey=http://host/path or -forceFlushAuthKey=https://host/path
-forceMergeAuthKey value
authKey, which must be passed in query string to /internal/force_merge . It overrides -httpAuth.* . See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/#forced-merge
Flag value can be read from the given file when using -forceMergeAuthKey=file:///abs/path/to/file or -forceMergeAuthKey=file://./relative/path/to/file.
Flag value can be read from the given http/https url when using -forceMergeAuthKey=http://host/path or -forceMergeAuthKey=https://host/path
-fs.disableMmap
Whether to use pread() instead of mmap() for reading data files. By default, mmap() is used for 64-bit arches and pread() is used for 32-bit arches, since they cannot read data files bigger than 2^32 bytes in memory. mmap() is usually faster for reading small data chunks than pread()
-fs.maxConcurrency int
The maximum number of concurrent goroutines to work with files; smaller values may help reducing Go scheduling latency on systems with small number of CPU cores; higher values may help reducing data ingestion latency on systems with high-latency storage such as NFS or Ceph (default 128)
-futureRetention value
Log entries with timestamps bigger than now+futureRetention are rejected during data ingestion; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/#retention
The following optional suffixes are supported: s (second), h (hour), d (day), w (week), y (year). If suffix isn't set, then the duration is counted in months (default 2d)
-http.connTimeout duration
Incoming connections to -httpListenAddr are closed after the configured timeout. This may help evenly spreading load among a cluster of services behind TCP-level load balancer. Zero value disables closing of incoming connections (default 2m0s)
-http.disableCORS
Disable CORS for all origins (*)
-http.disableKeepAlive
Whether to disable HTTP keep-alive for incoming connections at -httpListenAddr
-http.disableResponseCompression
Disable compression of HTTP responses to save CPU resources. By default, compression is enabled to save network bandwidth
-http.header.csp string
Value for 'Content-Security-Policy' header, recommended: "default-src 'self'"
-http.header.frameOptions string
Value for 'X-Frame-Options' header
-http.header.hsts string
Value for 'Strict-Transport-Security' header, recommended: 'max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains'
-http.idleConnTimeout duration
Timeout for incoming idle http connections (default 1m0s)
-http.maxGracefulShutdownDuration duration
The maximum duration for a graceful shutdown of the HTTP server. A highly loaded server may require increased value for a graceful shutdown (default 7s)
-http.pathPrefix string
An optional prefix to add to all the paths handled by http server. For example, if '-http.pathPrefix=/foo/bar' is set, then all the http requests will be handled on '/foo/bar/*' paths. This may be useful for proxied requests. See https://www.robustperception.io/using-external-urls-and-proxies-with-prometheus
-http.shutdownDelay duration
Optional delay before http server shutdown. During this delay, the server returns non-OK responses from /health page, so load balancers can route new requests to other servers
-httpAuth.password value
Password for HTTP server's Basic Auth. The authentication is disabled if -httpAuth.username is empty
Flag value can be read from the given file when using -httpAuth.password=file:///abs/path/to/file or -httpAuth.password=file://./relative/path/to/file.
Flag value can be read from the given http/https url when using -httpAuth.password=http://host/path or -httpAuth.password=https://host/path
-httpAuth.username string
Username for HTTP server's Basic Auth. The authentication is disabled if empty. See also -httpAuth.password
-httpListenAddr array
TCP address to listen for incoming http requests. See also -httpListenAddr.useProxyProtocol
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-httpListenAddr.useProxyProtocol array
Whether to use proxy protocol for connections accepted at the given -httpListenAddr . See https://www.haproxy.org/download/1.8/doc/proxy-protocol.txt . With enabled proxy protocol http server cannot serve regular /metrics endpoint. Use -pushmetrics.url for metrics pushing
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Empty values are set to false.
-inmemoryDataFlushInterval duration
The interval for guaranteed saving of in-memory data to disk. The saved data survives unclean shutdowns such as OOM crash, hardware reset, SIGKILL, etc. Bigger intervals may help increase the lifetime of flash storage with limited write cycles (e.g. Raspberry PI). Smaller intervals increase disk IO load. Minimum supported value is 1s (default 5s)
-insert.concurrency int
The average number of concurrent data ingestion requests, which can be sent to every -storageNode (default 2)
-insert.disable
Whether to disable /insert/* HTTP endpoints
-insert.disableCompression
Whether to disable compression when sending the ingested data to -storageNode nodes. Disabled compression reduces CPU usage at the cost of higher network usage
-insert.indexFlushInterval duration
Amount of time after which the index of a trace is flushed. VictoriaTraces creates an index for each trace ID based on its start and end times.Each trace ID must wait in the queue for -insert.indexFlushInterval, continuously updating its start and end times before being flushed into the index. (default 20s)
-insert.maxFieldsPerLine int
The maximum number of log fields per line, which can be read by /insert/* handlers; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victorialogs/faq/#how-many-fields-a-single-log-entry-may-contain (default 1000)
-insert.maxQueueDuration duration
The maximum duration to wait in the queue when -maxConcurrentInserts concurrent insert requests are executed (default 1m0s)
-internStringCacheExpireDuration duration
The expiry duration for caches for interned strings. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/String_interning . See also -internStringMaxLen and -internStringDisableCache (default 6m0s)
-internStringDisableCache
Whether to disable caches for interned strings. This may reduce memory usage at the cost of higher CPU usage. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/String_interning . See also -internStringCacheExpireDuration and -internStringMaxLen
-internStringMaxLen int
The maximum length for strings to intern. A lower limit may save memory at the cost of higher CPU usage. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/String_interning . See also -internStringDisableCache and -internStringCacheExpireDuration (default 500)
-internaldelete.enable
Whether to enable /internal/delete/* HTTP endpoints, which are used by vtselect for deleting spans via delete API at vtstorage nodes
-internalinsert.disable
Whether to disable /internal/insert HTTP endpoint. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/cluster/#security
-internalinsert.maxRequestSize size
The maximum size in bytes of a single request, which can be accepted at /internal/insert HTTP endpoint
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, TB, KiB, MiB, GiB, TiB (default 67108864)
-internalselect.disable
Whether to disable /internal/select/* HTTP endpoints
-logIngestedRows
Whether to log all the ingested trace spans; this can be useful for debugging of data ingestion; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/data-ingestion/ ; see also -logNewStreams
-logNewStreams
Whether to log creation of new streams; this can be useful for debugging of high cardinality issues with log streams; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/keyconcepts/#stream-fields ; see also -logIngestedRows
-logNewStreamsAuthKey value
authKey, which must be passed in query string to /internal/log_new_streams . It overrides -httpAuth.* . See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victorialogs/#logging-new-streams
Flag value can be read from the given file when using -logNewStreamsAuthKey=file:///abs/path/to/file or -logNewStreamsAuthKey=file://./relative/path/to/file.
Flag value can be read from the given http/https url when using -logNewStreamsAuthKey=http://host/path or -logNewStreamsAuthKey=https://host/path
-loggerDisableTimestamps
Whether to disable writing timestamps in logs
-loggerErrorsPerSecondLimit int
Per-second limit on the number of ERROR messages. If more than the given number of errors are emitted per second, the remaining errors are suppressed. Zero values disable the rate limit
-loggerFormat string
Format for logs. Possible values: default, json (default "default")
-loggerJSONFields string
Allows renaming fields in JSON formatted logs. Example: "ts:timestamp,msg:message" renames "ts" to "timestamp" and "msg" to "message". Supported fields: ts, level, caller, msg
-loggerLevel string
Minimum level of errors to log. Possible values: INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, PANIC (default "INFO")
-loggerMaxArgLen int
The maximum length of a single logged argument. Longer arguments are replaced with 'arg_start..arg_end', where 'arg_start' and 'arg_end' is prefix and suffix of the arg with the length not exceeding -loggerMaxArgLen / 2 (default 5000)
-loggerOutput string
Output for the logs. Supported values: stderr, stdout (default "stderr")
-loggerTimezone string
Timezone to use for timestamps in logs. Timezone must be a valid IANA Time Zone. For example: America/New_York, Europe/Berlin, Etc/GMT+3 or Local (default "UTC")
-loggerWarnsPerSecondLimit int
Per-second limit on the number of WARN messages. If more than the given number of warns are emitted per second, then the remaining warns are suppressed. Zero values disable the rate limit
-maxBackfillAge value
Trace spans with timestamps older than now-maxBackfillAge are rejected during data ingestion; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victorialogs/#backfilling
The following optional suffixes are supported: s (second), h (hour), d (day), w (week), y (year). If suffix isn't set, then the duration is counted in months (default 0)
-maxConcurrentInserts int
The maximum number of concurrent insert requests. Set higher value when clients send data over slow networks. Default value depends on the number of available CPU cores. It should work fine in most cases since it minimizes resource usage. See also -insert.maxQueueDuration (default 16)
-memory.allowedBytes size
Allowed size of system memory VictoriaMetrics caches may occupy. This option overrides -memory.allowedPercent if set to a non-zero value. Too low a value may increase the cache miss rate usually resulting in higher CPU and disk IO usage. Too high a value may evict too much data from the OS page cache resulting in higher disk IO usage
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, TB, KiB, MiB, GiB, TiB (default 0)
-memory.allowedPercent float
Allowed percent of system memory VictoriaMetrics caches may occupy. See also -memory.allowedBytes. Too low a value may increase cache miss rate usually resulting in higher CPU and disk IO usage. Too high a value may evict too much data from the OS page cache which will result in higher disk IO usage (default 60)
-metrics.exposeMetadata
Whether to expose TYPE and HELP metadata at the /metrics page, which is exposed at -httpListenAddr . The metadata may be needed when the /metrics page is consumed by systems, which require this information. For example, Managed Prometheus in Google Cloud - https://cloud.google.com/stackdriver/docs/managed-prometheus/troubleshooting#missing-metric-type
-metricsAuthKey value
Auth key for /metrics endpoint. It must be passed via authKey query arg. It overrides -httpAuth.*
Flag value can be read from the given file when using -metricsAuthKey=file:///abs/path/to/file or -metricsAuthKey=file://./relative/path/to/file.
Flag value can be read from the given http/https url when using -metricsAuthKey=http://host/path or -metricsAuthKey=https://host/path
-opentelemetry.traces.maxRequestSize size
The maximum size in bytes of a single OpenTelemetry trace export request.
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, TB, KiB, MiB, GiB, TiB (default 67108864)
-otlpGRPC.tls
Enable TLS for incoming gRPC request at the given -otlpGRPCListenAddr. It's set to true by default, and -otlpGRPC.tlsCertFile and -otlpGRPC.tlsKeyFile must be set. It could be configured to false to allow insecure connection. (default true)
-otlpGRPC.tlsCertFile string
Path to file with TLS certificate for the corresponding -otlpGRPCListenAddr if -otlpGRPC.tls is not set to false. Prefer ECDSA certs instead of RSA certs as RSA certs are slower. The provided certificate file is automatically re-read every second, so it can be dynamically updated.
-otlpGRPC.tlsCipherSuites array
Optional TLS cipher suites for incoming requests over HTTPS if -otlpGRPC.tls is not set to false. See the list of supported cipher suites at https://pkg.go.dev/crypto/tls#pkg-constants
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-otlpGRPC.tlsKeyFile string
Path to file with TLS key for the corresponding -otlpGRPCListenAddr if -otlpGRPC.tls is not set to false. The provided key file is automatically re-read every second, so it can be dynamically updated.
-otlpGRPC.tlsMinVersion string
Optional minimum TLS version to use for the corresponding -otlpGRPCListenAddr if -otlpGRPC.tls is not set to false. Supported values: TLS10, TLS11, TLS12, TLS13.
-otlpGRPCListenAddr string
TCP address for accepting OTLP gRPC requests. Defaults to empty, which means it is disabled. The recommended port is ":4317".
-partitionManageAuthKey value
authKey, which must be passed in query string to /internal/partition/* . It overrides -httpAuth.* . See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/#partitions-lifecycle
Flag value can be read from the given file when using -partitionManageAuthKey=file:///abs/path/to/file or -partitionManageAuthKey=file://./relative/path/to/file.
Flag value can be read from the given http/https url when using -partitionManageAuthKey=http://host/path or -partitionManageAuthKey=https://host/path
-pprofAuthKey value
Auth key for /debug/pprof/* endpoints. It must be passed via authKey query arg. It overrides -httpAuth.*
Flag value can be read from the given file when using -pprofAuthKey=file:///abs/path/to/file or -pprofAuthKey=file://./relative/path/to/file.
Flag value can be read from the given http/https url when using -pprofAuthKey=http://host/path or -pprofAuthKey=https://host/path
-pushmetrics.disableCompression
Whether to disable request body compression when pushing metrics to every -pushmetrics.url
-pushmetrics.extraLabel array
Optional labels to add to metrics pushed to every -pushmetrics.url . For example, -pushmetrics.extraLabel='instance="foo"' adds instance="foo" label to all the metrics pushed to every -pushmetrics.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-pushmetrics.header array
Optional HTTP request header to send to every -pushmetrics.url . For example, -pushmetrics.header='Authorization: Basic foobar' adds 'Authorization: Basic foobar' header to every request to every -pushmetrics.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-pushmetrics.interval duration
Interval for pushing metrics to every -pushmetrics.url (default 10s)
-pushmetrics.url array
Optional URL to push metrics exposed at /metrics page. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/single-server-victoriametrics/#push-metrics . By default, metrics exposed at /metrics page aren't pushed to any remote storage
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-retention.maxDiskSpaceUsageBytes size
The maximum disk space usage at -storageDataPath before older per-day partitions are automatically dropped; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/#retention-by-disk-space-usage ; see also -retentionPeriod
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, TB, KiB, MiB, GiB, TiB (default 0)
-retention.maxDiskUsagePercent int
The maximum allowed disk usage percentage (1-100) for the filesystem that contains -storageDataPath before older per-day partitions are automatically dropped; mutually exclusive with -retention.maxDiskSpaceUsageBytes; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/#retention-by-disk-space-usage-percent
-retentionPeriod value
Trace spans with timestamps older than now-retentionPeriod are automatically deleted; trace spans with timestamps outside the retention are also rejected during data ingestion; the minimum supported retention is 1d (one day); see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/#retention ; see also -retention.maxDiskSpaceUsageBytes and -retention.maxDiskUsagePercent
The following optional suffixes are supported: s (second), h (hour), d (day), w (week), y (year). If suffix isn't set, then the duration is counted in months (default 7d)
-search.allowPartialResponse
Whether to allow returning partial responses when some of vtstorage nodes from the -storageNode list are unavailable for querying. This flag works only for cluster setup of VictoriaLogs. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victorialogs/querying/#partial-responses
-search.latencyOffset duration
The time when a trace become visible in query results after the collection. see -insert.traceMaxDuration as well. (default 30s) (default 30s)
-search.logSlowQueryDuration duration
Log queries with execution time exceeding this value. Zero disables slow query logging (default 5s)
-search.maxConcurrentRequests int
The maximum number of concurrent search requests. It shouldn't be high, since a single request can saturate all the CPU cores, while many concurrently executed requests may require high amounts of memory. See also -search.maxQueueDuration (default 8)
-search.maxQueryDuration duration
The maximum duration for query execution. It can be overridden to a smaller value on a per-query basis via 'timeout' query arg (default 30s)
-search.maxQueryTimeRange value
The maximum time range, which can be set in the query sent to querying APIs. Queries with bigger time ranges are rejected. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victorialogs/querying/#resource-usage-limits
The following unit suffixes are required: s (second), m (minute), h (hour), d (day), w (week), y (year). Bare numbers without units are not allowed (except 0) (default 0)
-search.maxQueueDuration duration
The maximum time the search request waits for execution when -search.maxConcurrentRequests limit is reached; see also -search.maxQueryDuration (default 10s)
-search.traceMaxDurationWindow duration
The window of searching for the rest trace spans after finding one span.It allows extending the search start time and end time by -search.traceMaxDurationWindow to make sure all spans are included.It affects both Jaeger's /api/traces and /api/traces/<trace_id> APIs. (default 1m0s)
-search.traceMaxServiceNameList uint
The maximum number of service name can return in a get service name request. This limit affects Jaeger's /api/services API. (default 1000)
-search.traceMaxSpanNameList uint
The maximum number of span name can return in a get span name request. This limit affects Jaeger's /api/services/*/operations API. (default 1000)
-search.traceSearchStep duration
Splits the [0, now] time range into many small time ranges by -search.traceSearchStep when searching for spans by trace_id. Once it finds spans in a time range, it performs an additional search according to -search.traceMaxDurationWindow and then stops. It affects Jaeger's /api/traces/<trace_id> API. (default 24h0m0s)
-search.traceServiceAndSpanNameLookbehind duration
The time range of searching for service name and span name. It affects Jaeger's /api/services and /api/services/*/operations APIs. (default 72h0m0s)
-secret.flags array
Comma-separated list of flag names with secret values. Values for these flags are hidden in logs and on /metrics page
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-select.disable
Whether to disable /select/* HTTP endpoints
-select.disableCompression
Whether to disable compression for select query responses received from -storageNode nodes. Disabled compression reduces CPU usage at the cost of higher network usage
-servicegraph.enableTask
Whether to enable background task for generating service graph. It should only be enabled on VictoriaTraces single-node or vtstorage.
-servicegraph.taskInterval duration
The background task interval for generating service graph data. It requires setting -servicegraph.enableTask=true. (default 1m0s)
-servicegraph.taskLimit uint
How many service graph relations each task could fetch for each tenant. It requires setting -servicegraph.enableTask=true. (default 1000)
-servicegraph.taskLookbehind duration
The lookbehind window for each time service graph background task run. It requires setting -servicegraph.enableTask=true. (default 1m0s)
-servicegraph.taskTimeout duration
The background task timeout duration for generating service graph data. It requires setting -servicegraph.enableTask=true. (default 30s)
-storage.minFreeDiskSpaceBytes size
The minimum free disk space at -storageDataPath after which the storage stops accepting new data
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, TB, KiB, MiB, GiB, TiB (default 10000000)
-storageDataPath string
Path to directory where to store VictoriaTraces data; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriatraces/#storage (default "victoria-traces-data")
-storageNode array
Comma-separated list of TCP addresses for storage nodes to route the ingested spans to and to send select queries to. If the list is empty, then the ingested spans are stored and queried locally from -storageDataPath
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.bearerToken array
Optional bearer auth token to use for the corresponding -storageNode
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.bearerTokenFile array
Optional path to bearer token file to use for the corresponding -storageNode. The token is re-read from the file every second
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.password array
Optional basic auth password to use for the corresponding -storageNode
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.passwordFile array
Optional path to basic auth password to use for the corresponding -storageNode. The file is re-read every second
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.tls array
Whether to use TLS (HTTPS) protocol for communicating with the corresponding -storageNode. By default communication is performed via HTTP
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Empty values are set to false.
-storageNode.tlsCAFile array
Optional path to TLS CA file to use for verifying connections to the corresponding -storageNode. By default, system CA is used
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.tlsCertFile array
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate file to use when connecting to the corresponding -storageNode
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.tlsInsecureSkipVerify array
Whether to skip tls verification when connecting to the corresponding -storageNode
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Empty values are set to false.
-storageNode.tlsKeyFile array
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate key to use when connecting to the corresponding -storageNode
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.tlsServerName array
Optional TLS server name to use for connections to the corresponding -storageNode. By default, the server name from -storageNode is used
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.username array
Optional basic auth username to use for the corresponding -storageNode
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-storageNode.usernameFile array
Optional path to basic auth username to use for the corresponding -storageNode. The file is re-read every second
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-tls array
Whether to enable TLS for incoming HTTP requests at the given -httpListenAddr (aka https). -tlsCertFile and -tlsKeyFile must be set if -tls is set. See also -mtls
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Empty values are set to false.
-tlsCertFile array
Path to file with TLS certificate for the corresponding -httpListenAddr if -tls is set. Prefer ECDSA certs instead of RSA certs as RSA certs are slower. The provided certificate file is automatically re-read every second, so it can be dynamically updated. See also -tlsAutocertHosts
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-tlsCipherSuites array
Optional list of TLS cipher suites for incoming requests over HTTPS if -tls is set. See the list of supported cipher suites at https://pkg.go.dev/crypto/tls#pkg-constants
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-tlsKeyFile array
Path to file with TLS key for the corresponding -httpListenAddr if -tls is set. The provided key file is automatically re-read every second, so it can be dynamically updated. See also -tlsAutocertHosts
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-tlsMinVersion array
Optional minimum TLS version to use for the corresponding -httpListenAddr if -tls is set. Supported values: TLS10, TLS11, TLS12, TLS13
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Each array item can contain comma inside single-quoted or double-quoted string, {}, [] and () braces.
-version
Show VictoriaMetrics version